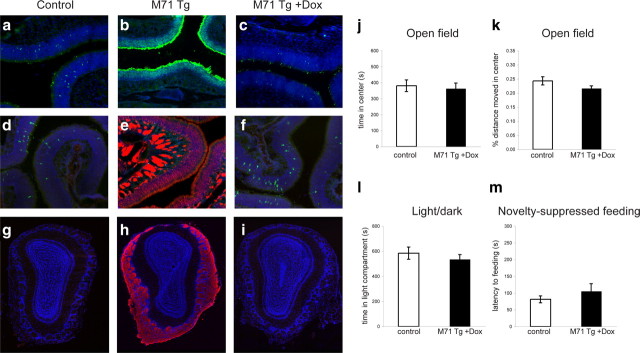
Figure 4.
Dox administration suppresses M71 transgene expression and rescues the anxiety-related behaviors in M71 transgenic mice. a–f, Histological analysis of Dox-mediated transgene suppression in sections through the MOE. a–c, Immunohistochemical detection of M71 OR-expressing cells in the MOE of control (a) and M71 transgenic (b) mice using anti-M71 antiserum (green). c, Neurons expressing the M71 OR in M71 transgenic mice maintained on Dox-infused food. d, Immunohistochemical detection of M50 OR-expressing cells (anti-M50 antiserum; green) in the MOE of control mice. e, Detection of M71 transgene expression using anti-lacZ antiserum (red) in the MOE of M71 transgenic mice. No M50 OR-expressing neurons could be detected in M71 transgenic mice. f, Detection of M50 OR-expressing neurons and suppression of M71 transgene expression in M71 transgenic mice maintained on Dox-infused food. g–i, Analysis of Dox-mediated transgene suppression in coronal sections through the olfactory bulb. Expression of M71-expressing fibers visualized by anti-lacZ antiserum can be detected in M71 transgenic mice (h), but not in control mice (g) or M71 transgenic mice maintained on Dox (i). Nuclear counterstain (TOTO-3) is shown in blue. j–m, Lack of anxiety-related behaviors in M71 transgenic mice maintained on Dox. j, k, Open field test (M71 transgenic mice: n = 15; M71 transgenic mice on Dox: n = 14). The time spent (j) and the percentage of distance moved (k) in the center of the arena is similar between M71 transgenic and control mice maintained on Dox. l, Light–dark choice test. No significant difference in the time spent in the light compartment was observed between M71 transgenic mice (n = 17) and controls (n = 13) maintained on Dox. m, Novelty-suppressed feeding. The latency to begin feeding was similar between M71 transgenic mice (n = 18) and controls (n = 13) maintained on Dox. Error bars are mean ± SEM.