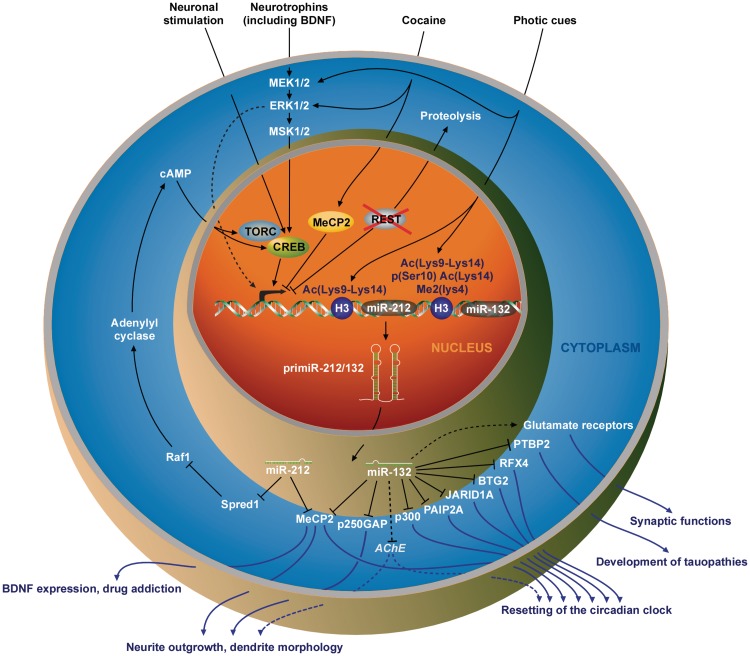
Figure 3.
Inducers and targets of the miR-212/132 locus in the neuronal compartment. In neurons, the transcriptional repressor REST is targeted to proteolysis, enabling the transcription of its target genes. Various stimuli (such as the exposition to neurotrophins or photic cues, or an extended access to cocaine) lead to the transcription of the miR-212/132 locus through CREB activation, although an unidentified ERK1/2-dependent, MSK1/2- and CREB-independent mechanism may also contribute to miR-212/132 expression in BDNF-stimulated neurons (dashed arrow). Histone 3 post-translational modifications are also involved in pri-miR-212/132 expression following light exposure. By repressing the expression of several mRNA targets (AChE is a probable but not yet demonstrated target of miR-132 in neurons), miR-212/132 are involved in neurite outgrowth and dendrite morphology as well as in the resetting of the circadian clock, and would participate to synaptic functions by up-regulating the expression of the glutamate receptors NR2A, NR2B and GluR1. miR-132 expression deregulation is also associated with the development of tauopathies through the targeting of PTBP2. Besides, miR-212 would be involved in regulating the vulnerability to cocaine addiction by targeting Spred1 mRNA.