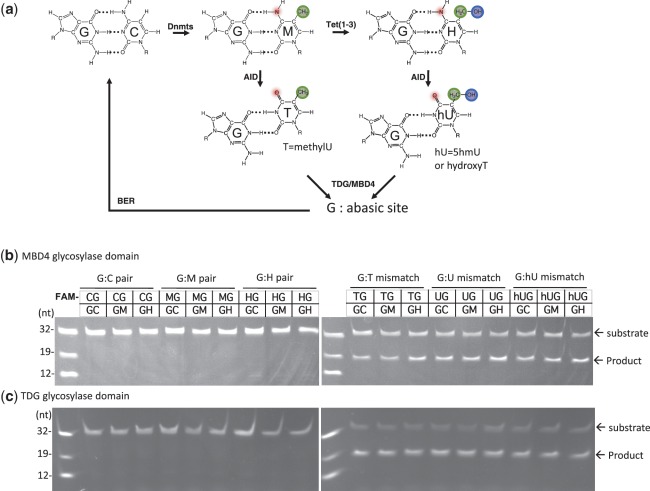
Figure 3.
MBD4 and TDG are capable of excising 5-hydroxymethyluracil in the context of a double-stranded CpG dinucleotide. (a) A putative pathway of DNA demethylation involving DNA methylation by DNMTs, hydroxylation by Tet proteins, deamination by AID and glycosylation by MBD4 or TDG linked to base excision repair (BER). Double stranded 32-bp oligonucleotides bearing a single CpG dinucleotide and the indicated modification status (where M = 5mC and H = 5hmC) and labeled with FAM on the top strand were incubated with the glycosylase domain of MBD4 (b) or TDG (c) at 37°C for 1 h. The products of the reaction were separated on a denaturing polyacrylamide gel, and the FAM-labeled strand was excited by UV and photographed.