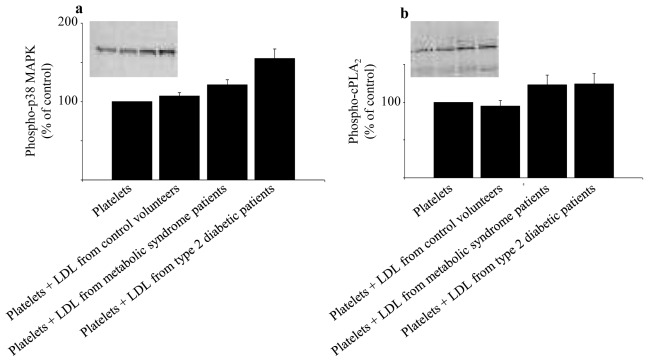
Fig. 2.
Effects of LDL from control volunteers, obese patients with MetS or type 2 diabetes on the phosphorylation of p38 MAPK (a) and cPLA2 (b) in platelets. Platelets from blood donors were incubated for 2h at 37°C in the absence or presence of LDL (1 mg protein/ml) from either control volunteers, MetS patients or type 2 diabetic patients. Representative immunoblots and histograms of the normalized amount of phosphorylation of p38 MAPK and cPLA2 are shown. Data are means ± SEM (7 to 8 subjects per group). Platelets + LDL from MetS patients vs platelets incubated with buffer : significantly different (p < 0.05) for phospho-p38 MAPK and phospho-cPLA2. Platelets + LDL from type 2 diabetic patients vs platelets incubated with buffer : significantly different for phospho-p38 MAPK (p < 0.01) and phospho-cPLA2 (p < 0.05). Platelets + LDL from type 2 diabetic patients vs platelets + LDL from MetS patients : significantly different for phospho-p38 MAPK (p < 0.05). p values were obtained by ANOVA followed by Fisher’s PLSD post hoc test. MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; cPLA2, cytosolic phospholipase A2.