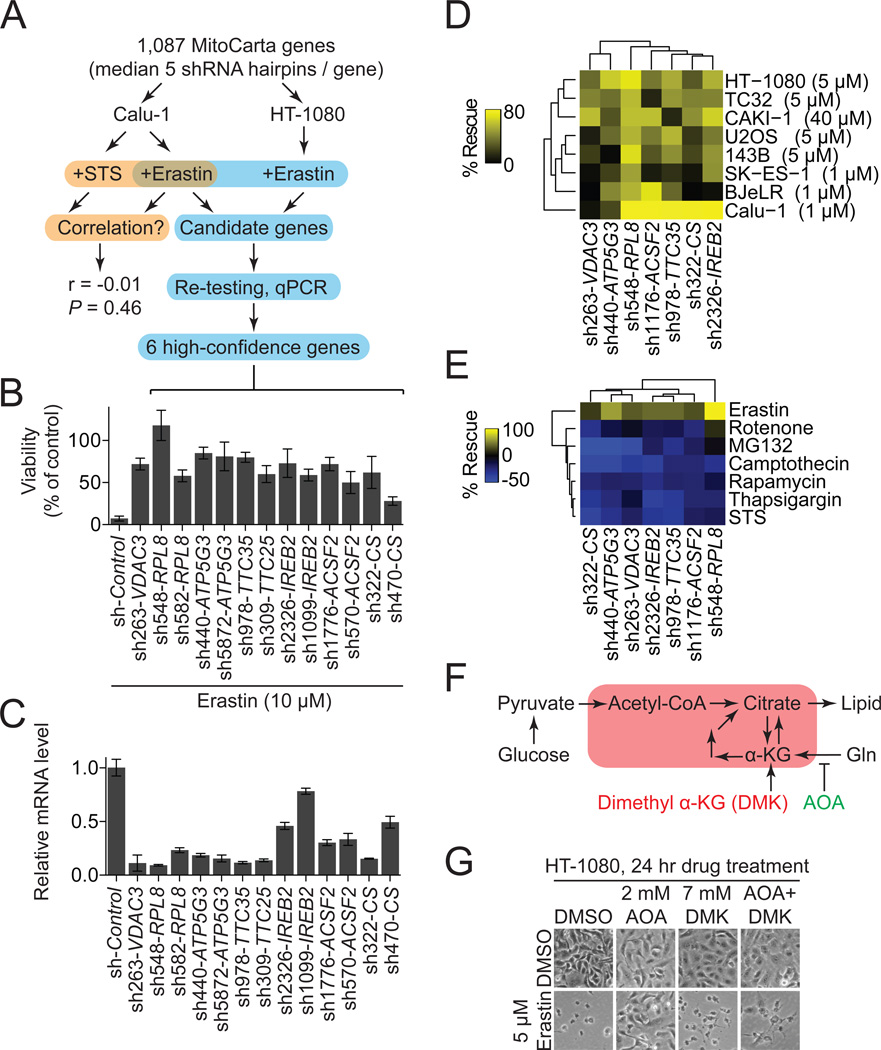
Figure 3. Erastin-induced ferroptosis exhibits a unique genetic profile.
(A) Outline of the MitoCarta shRNA screen and confirmation pipeline. (B,C) Six high confidence genes required for erastin-induced ferroptosis. (B) Viability of HT-1080 cells infected with shRNAs for 72 hours and treated with erastin (10 µM, 24 hrs). (C) mRNA levels for hairpins shown in (B) determined using RT-qPCR. Data in (B) and (C) are mean+/−SD from one of three experiments. (D,E) Effect of shRNA-mediated silencing of high-confidence genes using the best hairpin identified by mRNA silencing efficiency in (C) on cell viability. (E) Viability of various cell lines treated with a lethal dose of erastin (indicated in brackets) for 24 hours. (E) Viability of HT-1080 cells treated with various death-inducing or cytostatic compounds. For (D) and (E) % rescue was computed relative to each shRNA alone+DMSO. (F) Cartoon outline of glutamine (Gln) metabolism. Red box indicates mitochondria. (G) Images of HT-1080 cells treated with aminooxyacetic acid (AOA) +/− dimethyl alphaketoglutarate (DMK) +/− erastin.