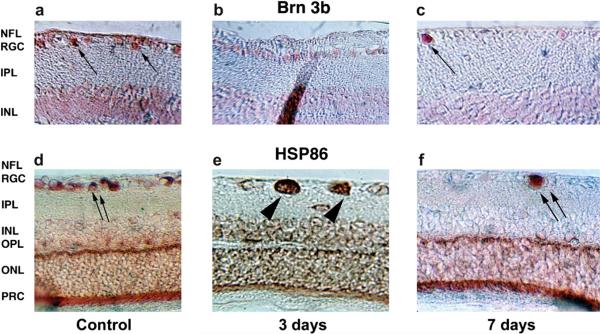
Fig. 14.
Intraretinal changes in protein expression. a–c: Brn-3b expression. d–f: HSP86 (HSP90α) expression. a. Baseline Brn-3b retinal expression. Brn-3b is concentrated in cells in the retinal ganglion cell (RGC) layer (arrows). Low background activity in the INL is due to cross-reactivity with other forms of Brn. b. Three days post-induction. Brn-3b protein in the RGC layer is reduced but still present. c. Seven days post-induction. There is loss of Brn-3b protein in many of the cells in the RGC layer, with continued strong expression in a few cells in this layer (arrow). d. HSP86 baseline expression. HSP86 is expressed at high levels in cells in the RGC layer (double arrows) and as a band in the outer plexiform layer (OPL). e. Three days post-induction. There is accumulation of HSP86 in individual swollen cells in the RGC layer (double arrowheads). There is a loss of HSP86 signal in the area of the OPL, with distribution of the signal throughout the retina. f. Seven days post-induction. HSP86 protein has disappeared in many of the cells in the RGC layer, with continued strong expression in a few cells in this layer (double arrows). There is reconstitution of the HSP86 signal in the OPL. NFL, nerve fiber layer; IPL, inner plexiform layer; INL, inner nuclear layer; ONL, outer nuclear layer; PRC, photoreceptors. Magnification: A–C: 400×, D–F: 200×.