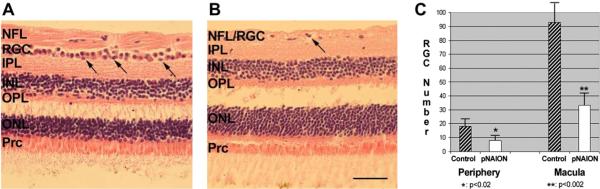
Fig. 21.
pNAION-associated histological changes in the retina. H&E staining. A. Control macular section. The RGC layer is packed with cells, with a double layer in some areas (arrows). The nerve fiber layer (NFL) is thick. B. Macular region 90 days post-pNAION. There is a loss of RGCs, with a few remaining nuclei (arrow). The NFL thickness is reduced. All other retinal layers are unchanged in both nuclear numbers and thickness. C. RGC quantification in peripheral region and macula. There is a statistically significant loss of RGCs in the superior retinal quadrant of the pNAION animal, compared with the control retina (one tailed t test, p < 0.02). RGC loss is greatest in the macula, where there is an average 65% RGC loss (p < 0.002) (mean ± s.d. of 6 sections/region). Scale bar: 50 microns.