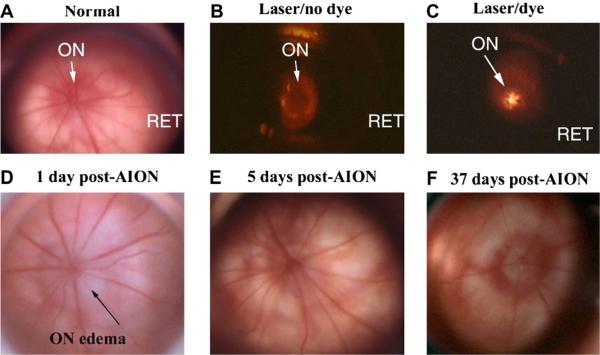
Fig. 8.
Comparison of retina and disk before, during and after rAION induction. Slit- lamp biomicroscopic view (high magnification) seen with rat fundus contact lens. A. control (pre-induced) rat optic nerve (ON) and retina RET. The ON is flat against the retina. Radial retinal vessels emerge from the ON to supply the inner retina. B. Laser exposure without RB dye administration. The ON is dark. C. Laser exposure after RB dye administration. The central vessels glow with a golden color, indicating dye activation. D. ON 1 day post-induction. ON edema is present, with ON pallor and obscuration of the disk margin. Retinal vascular dilation occurs in vessels emerging from the disk, suggesting that intrascleral ON edema has caused vascular compression, similar to that seen in human NAION. E. ON appearance 5 days post-induction. ON edema has resolved, with nearly normal appearance. F. ON appearance 37 days post-induction. The ON disk is pale and apparently reduced in size, suggesting atrophy and loss of vascularization. Choroidal vascularization surrounding the ON is intact.