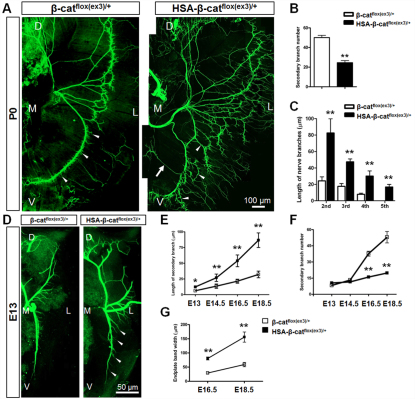
Fig. 2.
Aberrant innervation of motor axons in HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ mice. (A) P0 left hemi-diaphragms of indicated genotypes. Phrenic nerves and terminals were stained with anti-NF/synaptophysin antibodies, which were visualized with Alexa Fluor 488-conjugated goat anti-rabbit antibodies. (B) Decreased number of secondary/intramuscular nerve branches in HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ muscles (**P<0.01, n=7, t-test). (C) Increased length of secondary, tertiary, quaternary and 5th branches in HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ muscles (**P<0.01, n=6, one-way ANOVA). (D) E13 left hemi-diaphragms of indicated genotypes. (E) Increased secondary branch length in developing HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ embryos (*P<0.05, **P<0.01, n=5, one-way ANOVA). (F) Developmental changes of secondary branches in HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ embryos (**P<0.01, n=5, one-way ANOVA). (G) Increased endplate band width in E16.5 and E18.5 HSA-β-catflox(ex3)/+ embryos (**P<0.01, n=10, one-way ANOVA). In A and D, arrowheads indicate secondary nerve branches; arrow indicates ectopic axon. D, dorsal; V, ventral; L, lateral; M, medial. Error bars indicate s.e.m.