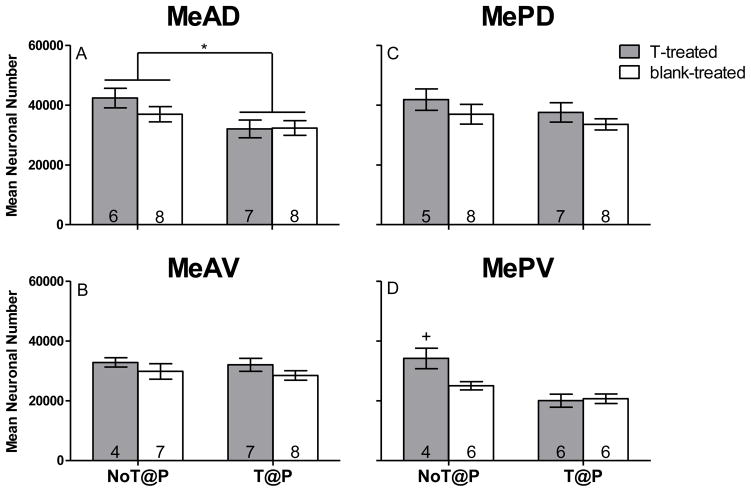
Figure 2.
Mean (±SEM) neuronal number of specific quadrants of the medial amygdala (Me) is testosterone-dependent in adult male Syrian hamsters. A: The presence of testosterone during puberty significantly increased neuronal number in the anterior dorsal Me (MeAD). B: There was no significant effect of testosterone on neuronal number in the anterior ventral Me (MeAV). C: There was no significant effect of testosterone on neuronal number in the posterior dorsal Me (MePD). D: There was an interaction between pubertal and adult testosterone on neuronal number in the posterior ventral Me (MePV), where adult testosterone significantly increased neuron number only in males that experienced the absence of pubertal testosterone (T-treated NoT@P). Numbers on bars indicate sample size. * indicates a significant difference between males that did not have testosterone during puberty (NoT@P) and males that did have testosterone during puberty (T@P) with p ≤ 0.05. +indicates an interaction between pubertal and adult testosterone with p ≤ 0.05.