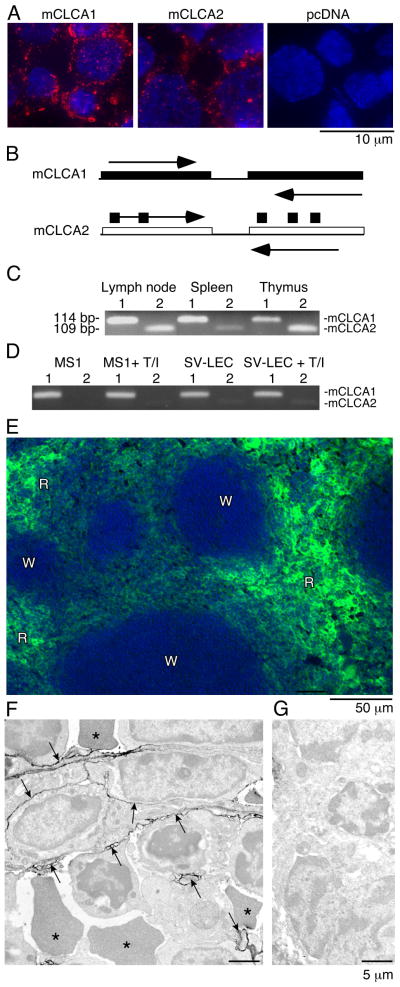
Figure 3. mCLCA1 is expressed in lymphatic endothelium and in lymphoid organs.
A). 10.1.1 antibody (red) stains cell membrane and cytoplasmic vesicles of 293 cells transfected with pcDNA-mCLCA1 or pcDNA-mCLCA2 expression constructs, with blue DAPI nuclear counterstaining. 293 cells transfected with pcDNA plasmid do not stain. B). PCR primers containing divergent sequences were used to specifically amplify the mCLCA1 or mCLCA2 cDNAs. C). RT-PCR of 114 bp mCLCA1 (1) or 109 bp mCLCA2 (2) identifies mCLCA1 and mCLCA2 mRNA expression in lymphoid organs. D). RT-PCR of mCLCA1 and mCLCA2 in MS1 and SV-LEC cells demonstrates that mCLCA1 is the major species in endothelial cells. TNFα/IL1β treatment for 48 h (T/I) does not alter mCLCA1 mRNA abundance. E). Spleen cryosections were immunostained for 10.1.1 antigen, revealing expression throughout the red pulp (R), but not the white pulp (W). F). Immunoperoxidase electron microscopy (Philips 201) of splenic red pulp immunostained with 10.1.1 antibody. The 10.1.1 antibody reactivity, evidenced by electron-dense peroxidase reaction product, is associated with stromal cell processes outlined by arrows, interspersed amongst leukocytes and red blood cells (*). G). No labeling is evident by electron microscopy when 10.1.1 antibody was replaced with normal hamster IgG.