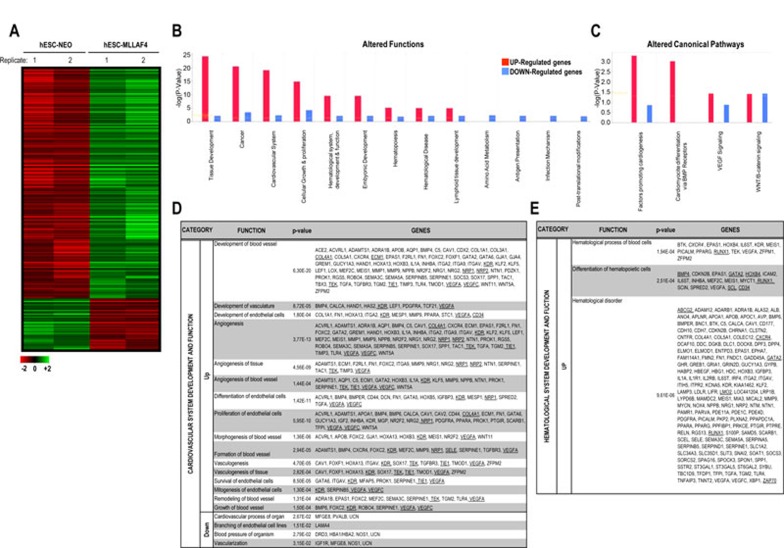
Figure 5.
Gene expression profiling and signaling pathways are altered in MLL-AF4 hESCs. (A) Heatmap showing a total of 1 267 genes differentially regulated between MLL-AF4 and NEO hESCs (P value < 0.05; 2-fold regulation). In all, 81% (1 015) of the genes differentially expressed are upregulated in MLL-AF4 hESCs. (B-E) After gene expression microarray analysis, the groups of genes differentially expressed (P value < 0.05; 2-fold regulation) in MLL-AF4 vs NEO hESCs were compared and the lists of functions and canonical pathways significantly altered were generated using the Ingenuity Pathways Analysis (IPA) 8 software. IPA software-based data mining generated a list of significantly modulated (up and down) gene functions (B) and canonical pathways (C) between MLL-AF4 and NEO hESCs. A more profound analysis was then performed for all the genes classified by the IPA software as involved in cardiovascular/vascular-endothelial system development and function (D) and hematopoietic system development and function (E). Master genes strongly associated with early hematopoiesis (i.e., SCL, RunX1, GATA2, CD34, BMP4, HOXB4) and vascular-endothelium (i.e., VEGFA, VEGFC, CD34, KDR, TIE1, TEK, SELE, NRP1, NRP2, COLs) likely to contribute to hemogenic precursor specification and subsequent endothelial development are underlined. Supplementary information, Table S1 contains the complete list of differentially regulated genes classified by the IPA software in the other gene functions and canonical pathways.