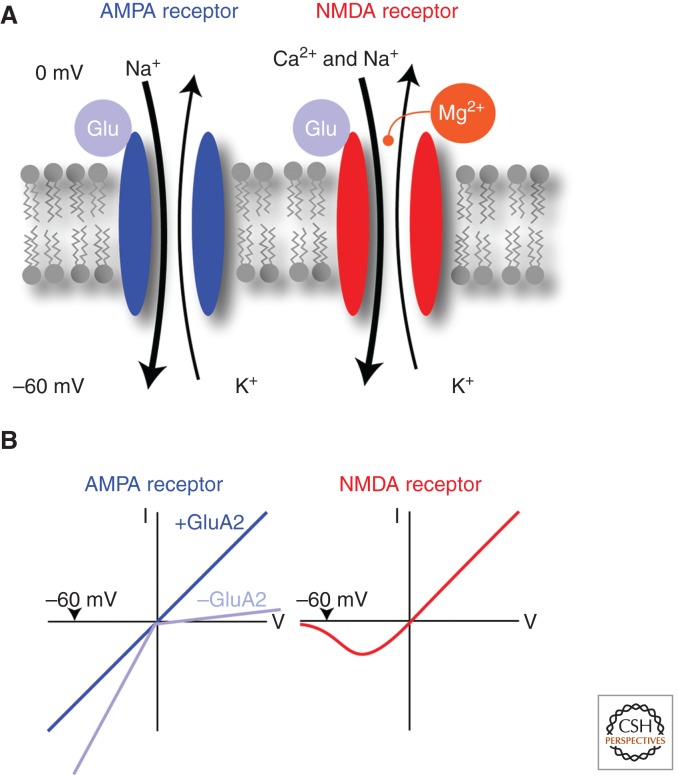
Figure 2.
Major ionotropic glutamate receptors involved in LTD and LTP. (A) When glutamate binds to AMPA receptors, many sodium ions flow into the cell while only some potassium ions leave the neuron, causing a net depolarization of the membrane. NMDA receptors are also permeable for calcium but only if the magnesium is expelled by a slight depolarization of the neuron. (B) The current–voltage (I–V) relationship provides a biophysical signature for the different receptors. AMPA receptors have a linear I–V relationship when they contain the subunit GluA2, but are inward-rectifying (see text for definition) without GluA2. NMDA receptors have a complex I–V curve because Mg blocks the pore at negative potentials.