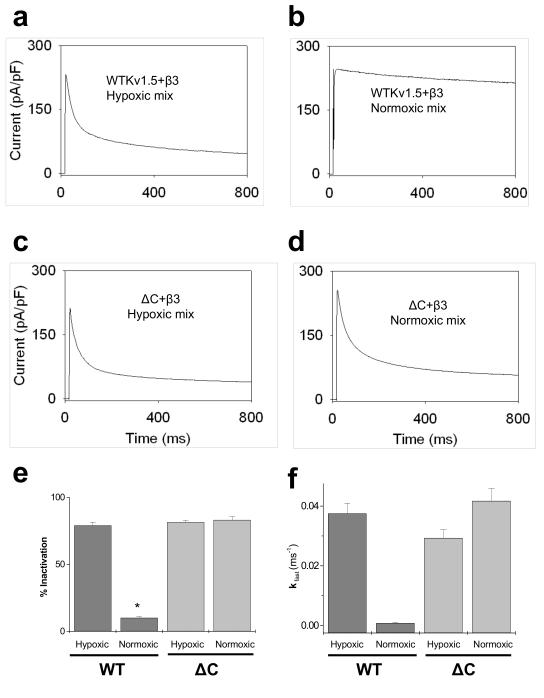
Fig. 6. Regulation of Kv currents by normoxic and hypoxic complement of pyridine nucleotides.
COS-7 cells co-expressing Kv1.5WT+Kvβ3 or Kv1.5ΔC+Kvβ3 were used for whole-cell patch-clamp recordings (n=5-8 cells). From a holding potential of −80mV the cells were depolarized to +50mV for 800 ms. Whole cell currents were recorded in (a, c) hypoxic and (b, d) normoxic mixture of nucleotides as indicated. The hypoxic complement of pyridine nucleotides consisted of the following: NADPH 80, NADP+ 50, NADH 1000, NAD+ 200 μM and the normoxic complement of pyridine nucleotides consisted of: NADPH 100, NADP+ 30, NADH 50, NAD+ 1000 μM in the patch pipette solution. Percent inactivation was calculated as percentage difference between the peak current and that at 800 ms and depicted as bar graph showing analysis from normoxic and hypoxic complements (e). Panel f shows the kfast of inactivation measured from the currents in hypoxic and normoxic groups. (*P<0.05 Normoxic vs. hypoxic within group)