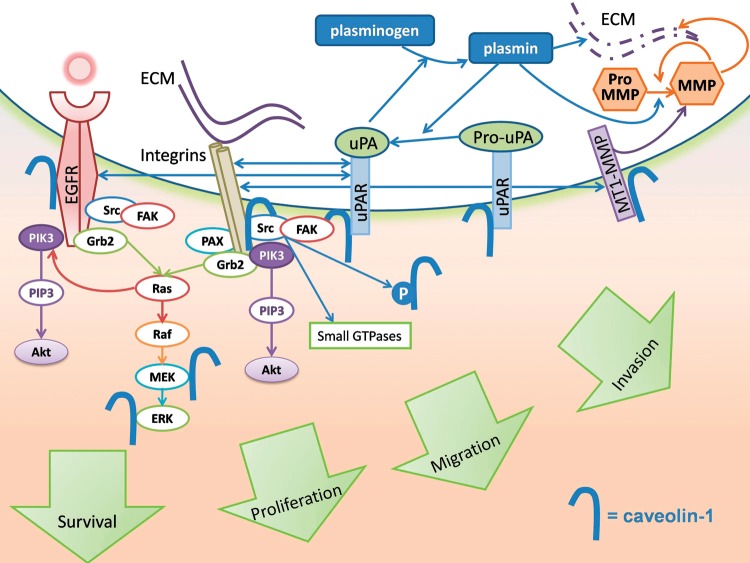
Fig. 1.
Multiple signaling pathways essential to GBM growth and invasion are controlled by caveolin-1. Receptor tyrosine kinases (EGFR), integrins, and uPA are concentrated in caveolae and interact with caveolin-1. Downstream signaling is initiated in caveolae. Caveolin-1 undergoes Src family kinase-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation upon EGF stimulation or integrin engagement. Caveolae endocytosis further controls EGFR presence at the cell surface. Binding to the caveolin-1 scaffolding domain inhibits and sequesters EGFR, as well as MT-1 MMP in caveolae. Caveolin-1 also directly inhibits MEK-1 and ERK-2 downstream of the EGFR activation. UPA forms a complex with integrins and caveolin-1 that signals through Src family kinases and focal adhesion kinase (FAK). Via interacting with the uPA receptor and MT1-MMP, caveolin-1 spatially controls extracellular proteolysis, including growth factor release from the extracellular matrix, and basement membrane degradation.