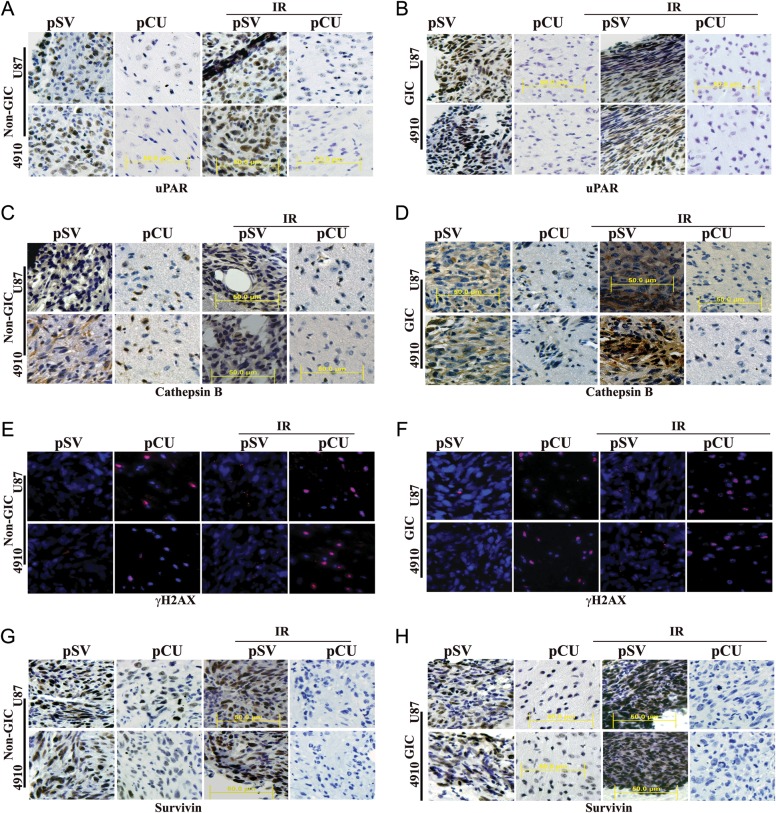
Fig. 7.
pCU combined with radiation enhanced DNA damage-induced apoptosis in vivo. (A–D) U87 and 4910 non-GICs and GICs (1 × 105) were injected intracranially into anesthetized nude mice. Tumors were allowed to grow for 1 week, and pCU and radiation treatments were given as described in Materials and Methods. Once the control animals showed chronic symptoms (3–4 weeks), the brains were harvested and sectioned. After deparaffinization, sections were immunoprobed for uPAR and cathepsin B using specific antibodies. After staining nuclei with DAPI, the slides were mounted and visualized under a confocal microscope. Immunohistochemical analysis of brain sections used anti-uPAR (A–B) and anti-cathepsin B antibodies (C–D). Sections were photographed (40X). (E–F) Sections were immunoprobed for γH2AX using specific antibodies, followed by appropriate Alexa Fluor-conjugated secondary antibodies. After staining nuclei with DAPI, the slides were mounted and visualized under a confocal microscope. (G–H) Immunohistochemical analysis of survivin in pCU-treated and pCU + radiation-treated brain tissue sections.