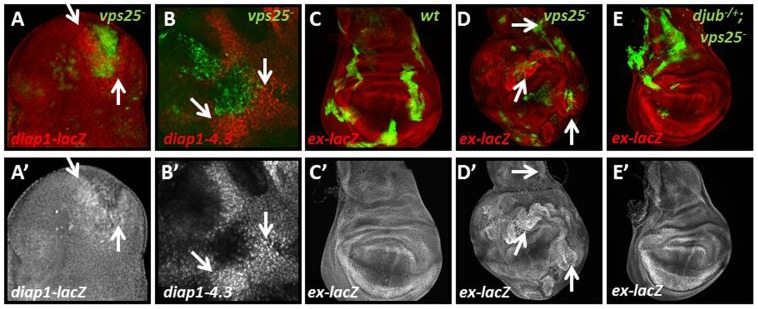
Figure 1. vps25 mutant cells can induce non-cell autonomous Yorkie activity.
Shown are mosaic imaginal discs. Control and vps25 mutant clones are marked in green. diap1-lacZ and ex-lacZ are detected by β-Gal labeling (red or grayscale). Arrows point to representative examples in the panels. (A,A’) vps25 mutant cells (green) induce non-cell autonomous diap1-lacZ expression (red and gray) in imaginal discs. (B,B’) vps25 mutant cells (green) induce non-cell autonomous Diap1-4.3GFP (red and grayscale). Please note that GFP is presented in red to match the color code in the other panels. vps25 mutant clones were identified by ubiquitylation-specific FK1/2 labeling which is known to be increased in vps25 mutant clones [14] (60×magnification). (C,C’) ex-lacZ expression (red and grayscale) in wild-type (wt) control mosaic wing discs. (D,D’) vps25 mutant cells (green) induce non-cell autonomous ex-lacZ in 71% of wing discs analyzed (n = 28) (red and grayscale). (E,E’) The non-cell autonomous induction of ex-lacZ (red and grayscale) by vps25 mutant clones (green) can be suppressed by removing one copy of djub (only 29% of wing discs still showed non-cell autonomous ex-lacZ (n = 28)). Genotypes: (A) yw hs-FLP; FRT42D Tub-Gal80/FRT42D vps25N55 y+; Tub-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/thj5c8 (B) yw hs-FLP; FRT42D piMyc/FRT42D vps25N55 y+; Diap1-4.3GFP/+ (C) yw hs-FLP; FRT42D Tub-Gal80/ex697 FRT42D y+; Tub-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/+ (D) yw hs-FLP; FRT42D Tub-Gal80/ex697 FRT42D vps25N55 y+; Tub-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/+ (E) yw hs-FLP/djubΔII; FRT42D Tub-Gal80/ex697 FRT42D vps25N55 y+; Tub-Gal4, UAS-CD8-GFP/+.