Fig. 2.
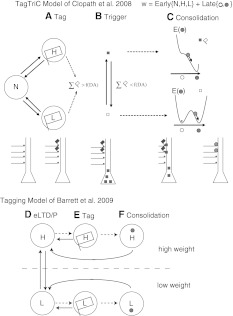
Models of synaptic consolidation. a–c TagTriC model by Clopath et al. (2008). The synaptic weight is a sum of the early-weight and the late-weight. The three phases of the model. a Tag: The early-weight can be in the neutral (N), low (L) or high (H) state. If in the H or L state, a tag is set (flag). b Trigger: If the number of tags exceed a threshold as of function of dopamine (DA), plasticity-related proteins are synthesized (squares). c Consolidation: If the synapse is tagged and plasticity-related proteins are available, the late-weight (circle) goes to the elevated stable state if the early-weight is in H or the low stable state if the early-weight is in L. E stands for the energy landscape of the late-weight, showing the two stable states unless the tag and the plasticity-related proteins are presents, then E only has one stable state. d–f Consolidation Model by Barrett et al. (2009). Each synapse has 2 possible states with 3 meta-states each, so 6 states in total. d The synapse can be in the early-state without tag, e early-state with the tag, or f consolidated state, each for both a low weight or a high weight. See original papers for details