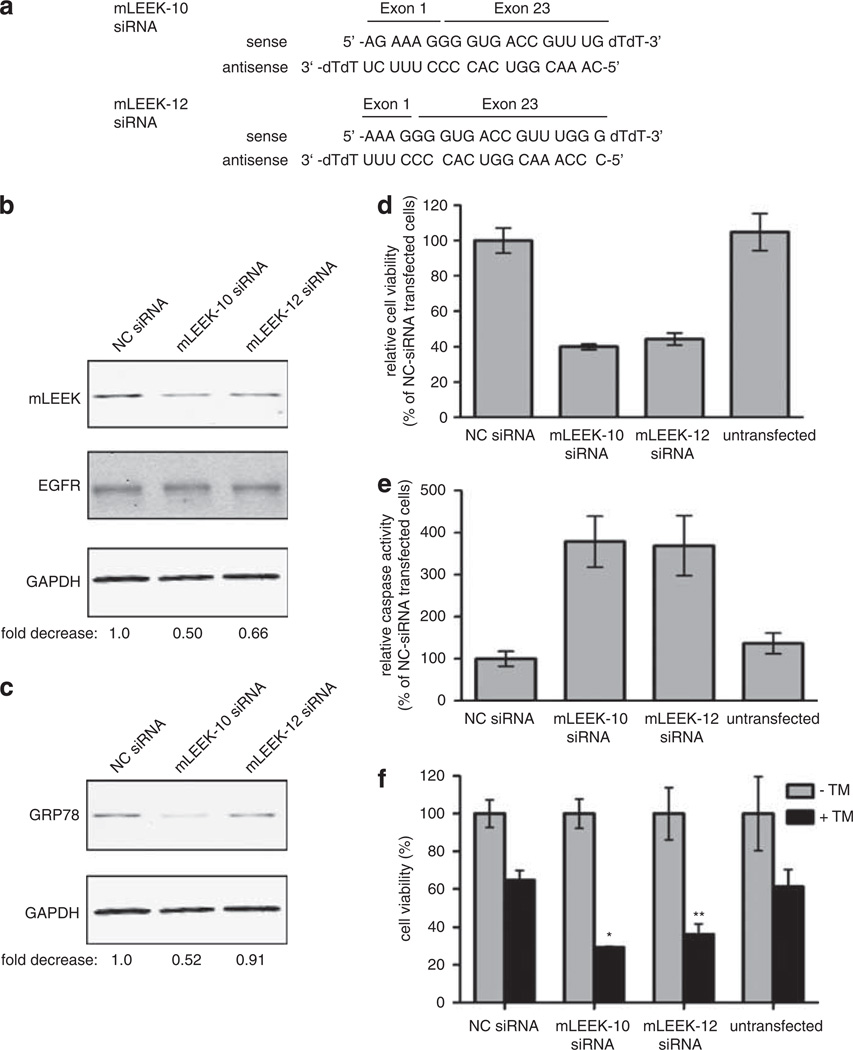
Figure 6.
mLEEK is essential for cell viability and mLEEK knockdown leads to caspase-mediated cell death and sensitization to ER stress. (a) Sequence of mLEEK-10 and mLEEK-12 siRNA. (b) Western blot of HeLa cells transiently transfected with mLEEK-10, mLEEK-12 or non-targeting control (NC) siRNA. Cells were harvested at 36 h and lysates blotted with indicated antibodies. Westerns were performed using fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies and detected with the Odyssey infrared imager. The signals from mLEEK and GAPDH were quantified and the ratio of mLEEK/GAPDH was determined. These ratios were normalized relative to the NC siRNA control (designated 1.0) to obtain the fold decrease. (c) Membranes from blots shown above were reprobed with anti-GRP78 antibody and quantified as above. (d) Decrease in HeLa cell viability as a result of mLEEK siRNA transfection. Cell viability was determined 72 h post-transfection using the CellTiter-Blue assay. Averages from three experiments are presented with s.d. values (bars). (e) Induction of apoptosis in cells transfected with mLEEK siRNA. Caspase-3/7 activity was measured 3 days after transfection using the Caspase-Glo 3/7 Assay. Values represent the average percentage of caspase 3/7 activity relative to that of NC siRNA-transfected cells. Results are averages with s.d. of four independent experiments. (f) HeLa cells were transfected with mLEEK-10, mLEEK-12 or non-targeting controls siRNA (NC). The cells were treated with tunicamycin or vehicle control for 24 h. Cell viability was determined as above. *P<0.001; **P<0.005, significantly different from the viability in Tm-treated non-targeting siRNA-transfected cells.