Figure 1.
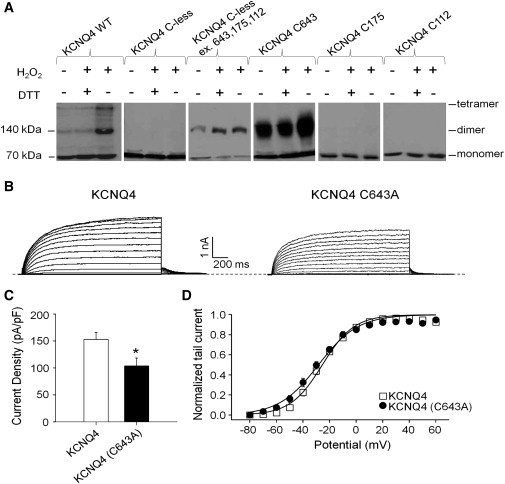
H2O2 induces oligomerization of KCNQ4 channels by intersubunit disulfide bonds between cysteines at the 643 position, but this residue is not a key factor in determining channel currents. (A) Representative immunoblots for cells transfected with the indicated WT or mutant myc-tagged KCNQ4 channels that were subjected to either sham rinse, H2O2 (500 μM, 15 min) alone, or H2O2 followed by DTT (2 mM, 15 min). (B) Representative perforated patch-clamp recordings from KCNQ4 and KCNQ4 (C643A). Cells were held at −80 mV and voltage steps were applied from −80 to 60 mV in 10 mV increments every 3 s. (C) Bars show summarized current densities at 60 mV for the indicated channels under perforated patch-clamp (n = 15–19; ∗p < 0.05). (D) Voltage dependence of activation measured from the normalized amplitudes of the tail currents at −60 mV, plotted as a function of test potential (n = 14–17).
