Figure 3.
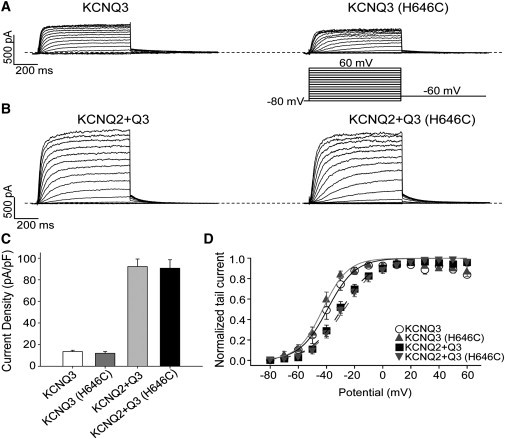
Effects of the H646C mutation on homomeric KCNQ3 and heteromeric KCNQ2 + Q3 currents. (A and B) Representative perforated patch-clamp recordings from cells transfected with WT KCNQ3, KCNQ3 (H646C), KCNQ2 + WT Q3, or KCNQ2 + Q3 (H646C). As shown in the inset, cells were held at −80 mV and voltage steps were applied from −80 to 60 mV in 10 mV increments. (C) Bars show summarized current densities at 60 mV for the indicated channels (n = 8–11). (D) Voltage dependence of activation measured from the normalized amplitudes of the tail currents at −60 mV, plotted as a function of test potential (n = 6–12).
