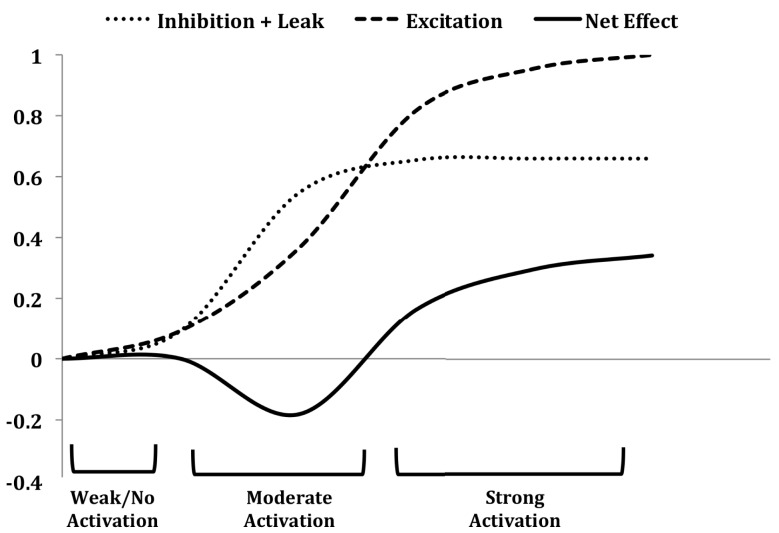
Figure 9.
The contrast enhancement function in mitral cells on the chip in response to sensor inputs. Mitral cells corresponding to moderately activated sensors are predominantly inhibited (reducing the spike rate of some cells to nearly 20% below baseline activity) by feed-forward PGo inhibition (moderate activation), whereas mitral cells excited by strongly activated sensors overcome the saturated PGo inhibition and exhibit net excitation (strong activation). The leak portion of the “inhibition + leak” curve represents charge leakage out of the cell between successive excitatory spikes received from OSN inputs, and therefore is inversely related to the activity of the OSNs. For strongly activated sensors, the excitation delivered to the mitral cells is of sufficiently high frequency to overcome the combined effects of PGo inhibition and the leak current. Figure adapted from Cleland and Sethupathy (2006).