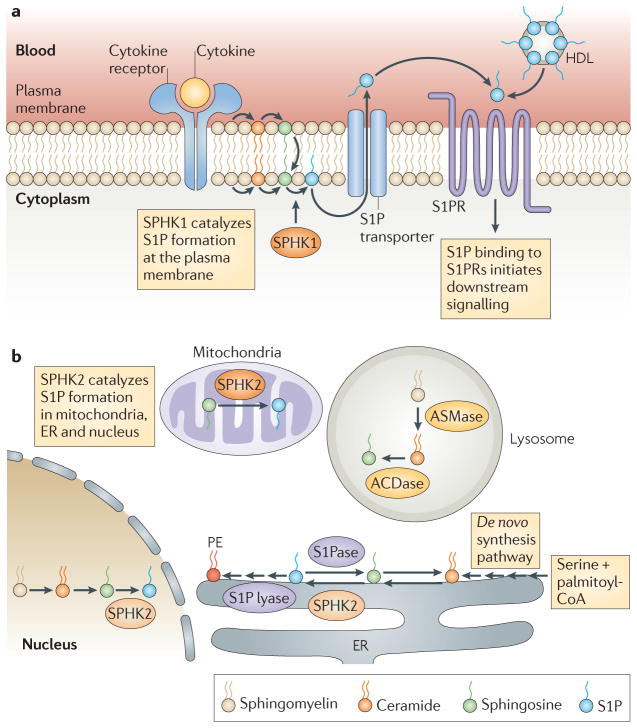
Figure 1. A simplified scheme of S1P synthesis and metabolism and inside-out signalling.
Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is synthesized by phosphorylation of sphingosine in a reaction that is catalysed by sphingosine kinase 1 (SPHK1) at the plasma membrane (a) and by SPHK2 at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), mitochondria and nucleus (b). At the ER, S1P is irreversibly degraded by S1P lyase or dephosphorylated to sphingosine by an S1P phosphatase (S1Pase). S1P produced at the plasma membrane in response to stimuli is released by specific transporters and regulates immune functions by binding to specific S1P receptors (S1PRs) and initiating downstream signalling pathways (inside-out signalling). S1P produced in the mitochondria and nucleus by SPHK2 has direct intracellular targets, and S1P generated by SPHK1 at the plasma membrane can also function intracellularly. In the blood, S1P is produced mainly by erythrocytes, is bound to albumin and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) and can activate S1PRs. ACDase, acid ceramidase; ASMase, acid sphingomyelinase.