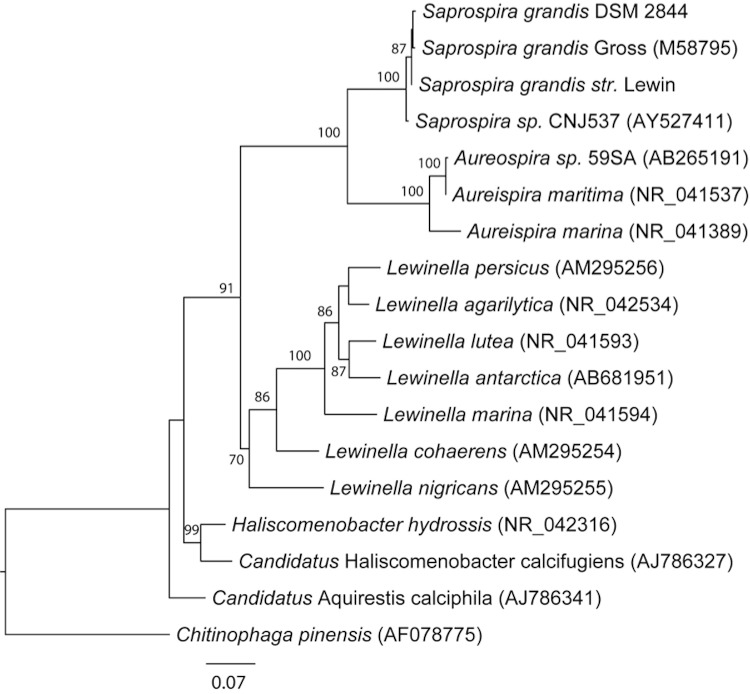
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of Saprospira grandis strain Lewin relative to other type and non-type strains within the Saprospiraceae. The tree was inferred from 1,350 aligned characters of the 16S rRNA gene sequence using maximum likelihood method. The branch lengths indicate the expected number of substitutions per site and the numbers adjacent to the branches are support values from 1,000 bootstrap replicates. Bootstrap values are indicated only if they are larger than 60%. Best topology of the tree was inferred by the phylogenetic analysis tool RAxML using GTR (General Time Reversible) model of substitution with the gamma model of rate heterogeneity [21]. Chitinophaga pinensis 16S rRNA gene was used to root the tree.