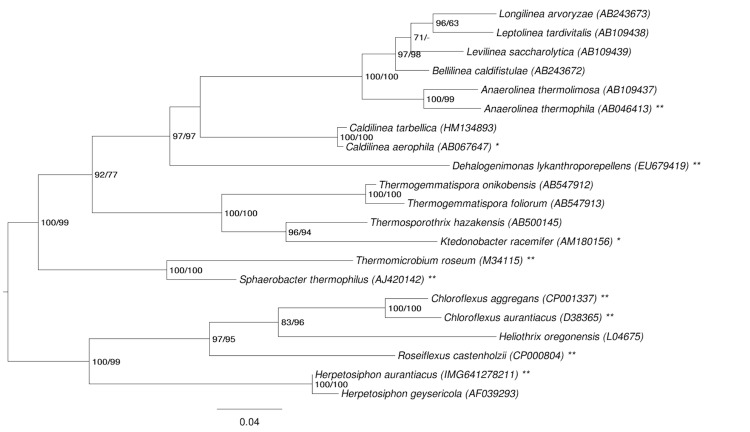
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree highlighting the position of H. aurantiacus relative to the other type strains within the phylum Chloroflexi. The tree was inferred from 1,350 aligned characters [11,12] of the 16S rRNA gene sequence under the maximum likelihood (ML) criterion [13]. Rooting was done initially using the midpoint method [14] and then checked for its agreement with the current classification (Table 1). The branches are scaled in terms of the expected number of substitutions per site. Numbers adjacent to the branches are support values from 100 ML bootstrap replicates [15] (left) and from 1,000 maximum parsimony bootstrap replicates [16] (right) if the value is larger than 60%. Lineages with type strain genome sequencing projects registered in GOLD [17] are labeled with one asterisk, and those also listed as 'Complete and Published' with two asterisks (see [18,19] and AP012029 for Anaerolinea thermophila, CP002084 for Dehalogenimonas lykanthroporepellens, CP001337 for Chloroflexus aggregans, CP000909 C. aurantiacus, and CP000804 for Roseiflexus castenholzii).