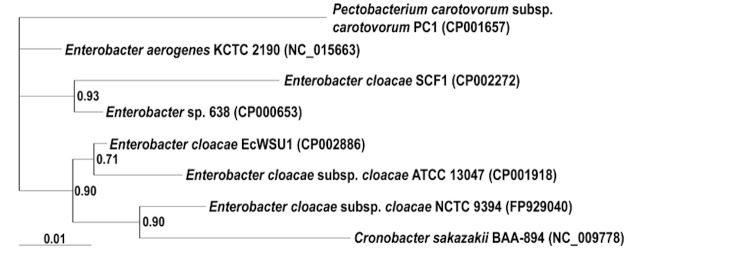
Figure 1.
Phylogenetic tree of 16S rRNA sequences from strains of Enterobacter with genome sequences. Bayesian phylogenetic analyses of the 16S rRNA region yielded two distinct clusters, supported with a 0.90 posterior probability. Analyses were implemented in MRBAYES [24]. The Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC), DT-ModSel [25] was used to determine the nucleotide substitution model best suited for the dataset. The Markov chain Monte Carlo search included two runs with four chains each for 1,000,000 generations, ensuring that the average split frequencies between the runs was less than 1%. Pectobacterium served as the outgroup for the analysis. Numbers in parentheses behind the bacterial names correspond to the Genbank accession numbers for the genome sequences. The scale bar indicates the number of substitutions/site.