Figure 1.
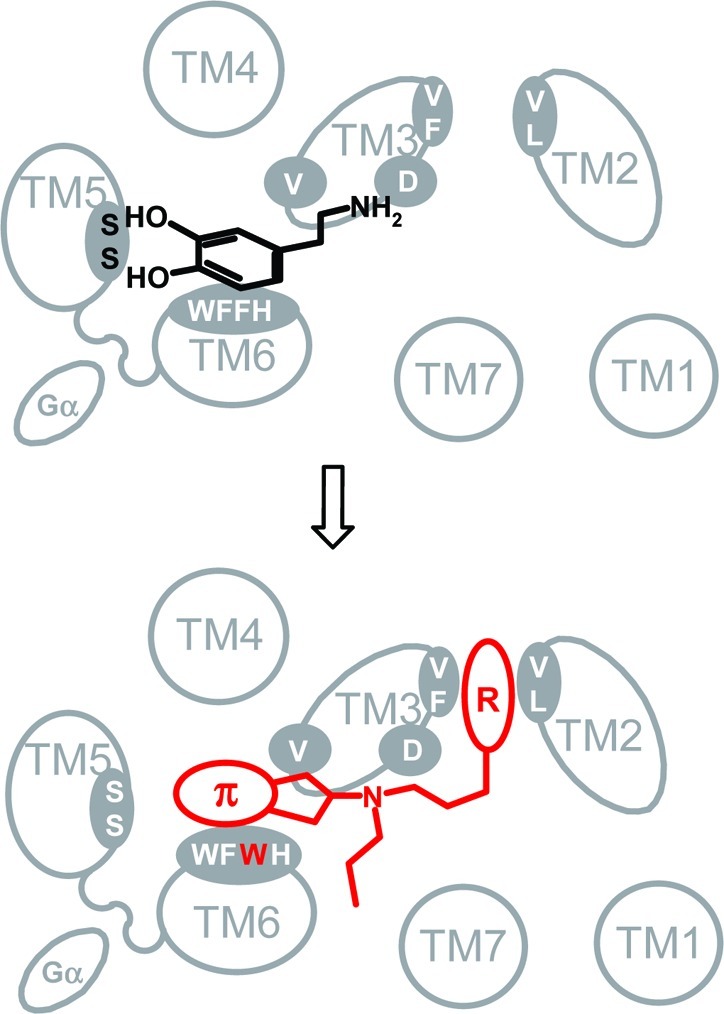
The primary binding site of D2 is expected to be lined by the highly conserved amino acids D3.32, V3.33 S5.42, S5.46, W6.48, F6.51, F6.52, and H6.55. Hydrogen bonds between the aromatic hydroxyl groups of dopamine and S5.42 and S5.46 in TM5 substantially contribute to the binding energy of dopamine. Mutation of phenylalanine to a bulky tryptophan at position 6.52 sterically interferes with this stabilization leading to a significant weakening of the binding of dopamine. An aminoindane moiety, forgoing H-bonding, is more flexible and, thus, can better tolerate local steric modifications. Molecular appendages (R) can be attracted by hydrophobic interactions with a secondary binding site provided by F3.28, V3.29, V2.61, and L2.64.
