Fig. 3.
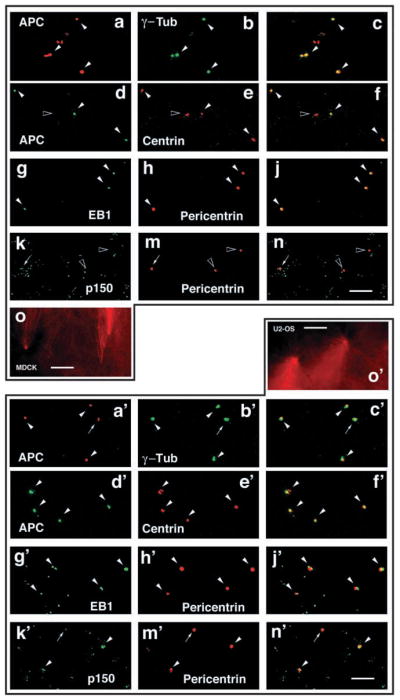
EB1 and its C-terminal binding partner APC co-purify with centrosomes. Centrosomes were purified from nocodazole-treated MDCK cells (a–o) or U-2 OS cells (a′–o′), stained for the centrosome markers γ-tubulin (green in a–c,a′–c′), centrin (red in d–f,d′–f′) or pericentrin (red in g–n,g′–n′) and co-stained for APC (red in a–c,a′–c′ and green in d–f,d′–f′), EB1 (green in g–j,g′–j′) or p150Glued/dynactin (green in k–n,k′–n′). Most of the purified centrosomes contain APC and EB1 (white arrowheads in a–j,a′–j′). An example of a centrosome without APC is shown (black arrowhead in d–f). By contrast, most of the centrosomes have little p150Glued/dynactin (arrows in k–n,k′–n′) or no p150Glued/dynactin (black arrowheads in k–n). Examples of centrosomes that contain p150Glued/dynactin are shown (white arrowheads in k′–n′). Purified MDCK (o) or U-2 OS (o′) centrosomes are functional as measured by induction of MT aster formation in vitro (o,o′). Bar, 10 μm.
