Fig. 5.
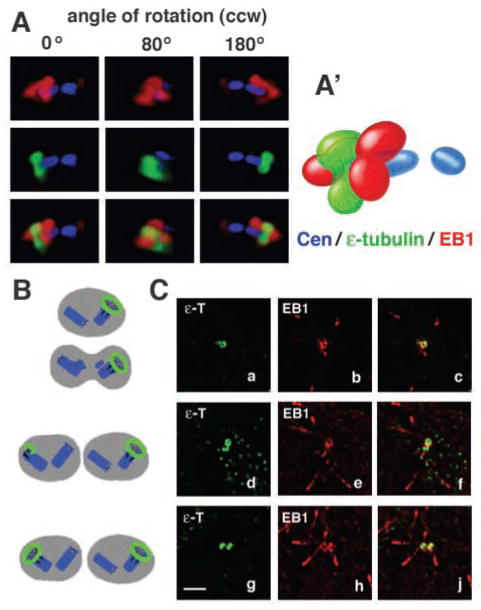
EB1 localizes to the mother centriole. (A) Centrosome region of a nocodazole-treated U-2 OS cell expressing GFP-centrin as a marker for centrioles (blue) and co-immunostained for EB1 (red) and for the mother centriole with ε-tubulin (green). Sections of this region were deconvolved and recombined in a 3D rendering. Multiple angles of a counterclockwise (ccw) rotation show that EB1 localizes with ε-tubulin to one end of the mother centriole. EB1 caps this end of the mother centriole like a wizard’s hat, whereas ε-tubulin forms a more ring-like structure around the same end. (A′) Schematic representation of 3D localization of proteins shown in A at the 0° angle. See Movie 3 (http://jcs.biologists.org/supplemental) for a 360° rotation and Materials and Methods for the resolution limits of the optical system. (B) Schematic representation of ε-tubulin distribution (green) during centrosome maturation as shown in the three panels in (C). (C) U-2 OS cell sections showing different centrosome maturation stages as marked by immunostaining for ε-tubulin (green in a,c,d,f,g,j). Sections are also stained for EB1 (red in b,c,e,f,h,j) to define EB1 localization during centrosome maturation. The first column shows increasing ε-tubulin accumulation at the second mother centriole (a,d,g). The second and third columns show that EB1 has a similar distribution pattern to ε-tubulin at different maturation stages (b–j) but that ε-tubulin precedes EB1 at the second mother centriole (c,f,j). In three out of 12 analysed cells, ε-tubulin was localized to the second centrosome, with EB1 being only at one centrosome. Bar, 2 μm.