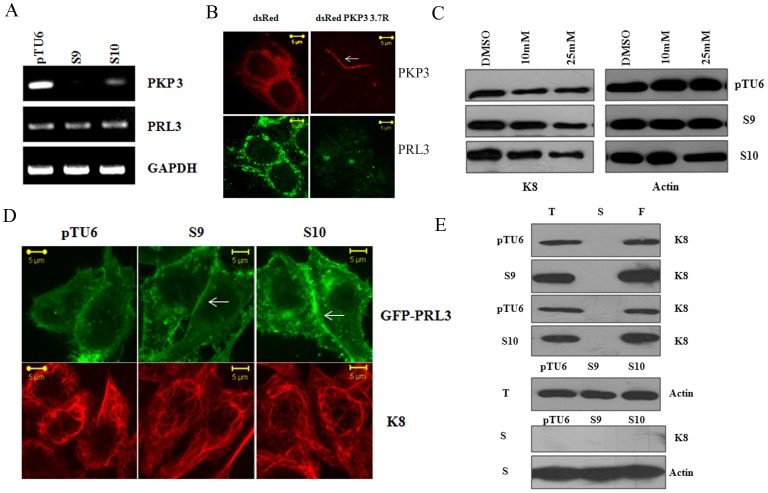
Figure 2. Plakophilin3 loss leads to an increase in PRL3 levels.
A. RNA prepared from the vector control or PKP3 knockdown clones was used as a template in reverse transcriptase coupled PCR reactions to determine the mRNA levels of PRL3 and PKP3. A PCR for GAPDH served as a loading control. B. S9 cells were transfected with either dsRed or the shRNA resistant dsRed PKP3 3.7R cDNA. 48 hours post transfection cells were stained with antibodies to PRL3 (green) and visualized by confocal microscopy. Note that dsRed PKP3 3.7R localizes to the border as previously described (indicated by arrow) [28]. Original magnification is 630X with a 2X optical zoom. Scale bar 5 µm. C. The vector control or PKP3 knockdown clones were treated with either the vehicle control (DMSO) or the indicated concentrations of the PRL3 inhibitor. Protein extracts were resolved on gels followed by Western blotting with antibodies to K8 and β-actin. D. GFP PRL3 was transfected into either vector control (pTU6) or PKP3 knockdown clones (S9 and S10). 48 hours post transfection, the cells were stained with antibodies to K8 (red) and visualized by confocal microscopy. Note that GFP PRL3 shows a marginally enhanced localization to the border in S9 and S10 cells in contrast to pTU6 and doesn’t show increased localization on K8 filaments. Original magnification is 630X with a 2X optical zoom. Scale bar 5 µm. E. Total cell extracts (T), Soluble fractions (S) and the filament fractions (F) were prepared as described from either the vector control or PKP3 knockdown clones. Equal cell equivalents of these extracts were loaded on 10% SDS-PAGE gels followed by Western blotting with antibodies to K8 (top four panels). A Western blot for β-actin was performed in the total cell extracts as a loading control (fifth panel). 100 µg of soluble fractions were resolved on SDS-PAGE gels followed by Western blotting for K8 or β-actin (bottom two panels).