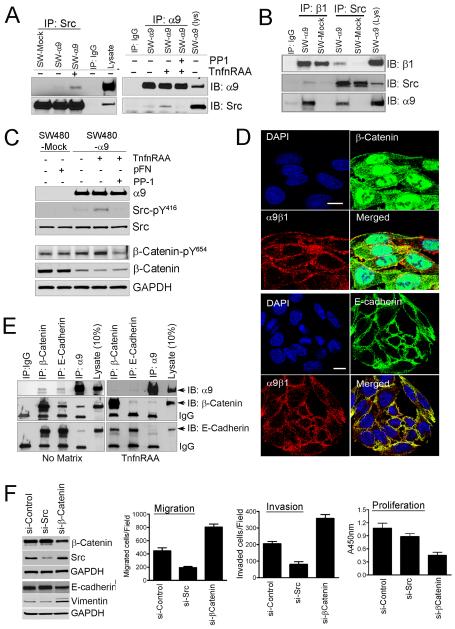
Figure-2. α9β1 co-associates with E-cadherin and β-catenin inducing EMT through src signaling.
A, Immunoblots for α9 or src from immunoprecipitates of SW480 cells cultured with or without the α9β1 specific ligand, TnfnRAA and/or the src inhibitor, PP1. B, Immunoblots for β1, α9 or Src from immunoprecipitates of matrix activated SW-480-mock (pFN) or SW480-α9 cells (TnfnRAA). C, Immunoblots for α9, Src or β-catenin in lysates from SW480-mock or α9 cells grown with pFN or TnfnRAA and/or PP1. D, Confocal images of SW480-α9 cells to determine co-localization of α9β1 (red) with β-catenin (green, top panel) or E-cadherin (green, bottom panel); nuclei stained blue with DAPI. E, Immunoblots, of immunoprecipitates from SW480-α9 grown on plastic (no matrix) or TnfnRAA (right panel), to determine co-association of α9 with β-catenin or E-cadherin. F, Left panel, Immunoblots for β-catenin, src, E-cadherin or vimentin in lysates from SW480-α9 cells transfected with non-targeted siRNA or siRNA targeted to src or β-catenin; Right panel: Migration (left), invasion (middle) or proliferation (right) assays in SW480-α9 cells following transfection with siRNA as indicated.