Figure 9. Putative scheme for the influence of high salt on nNOS and oxidative stress within the renal cortex of the mRen2.Lewis rat.
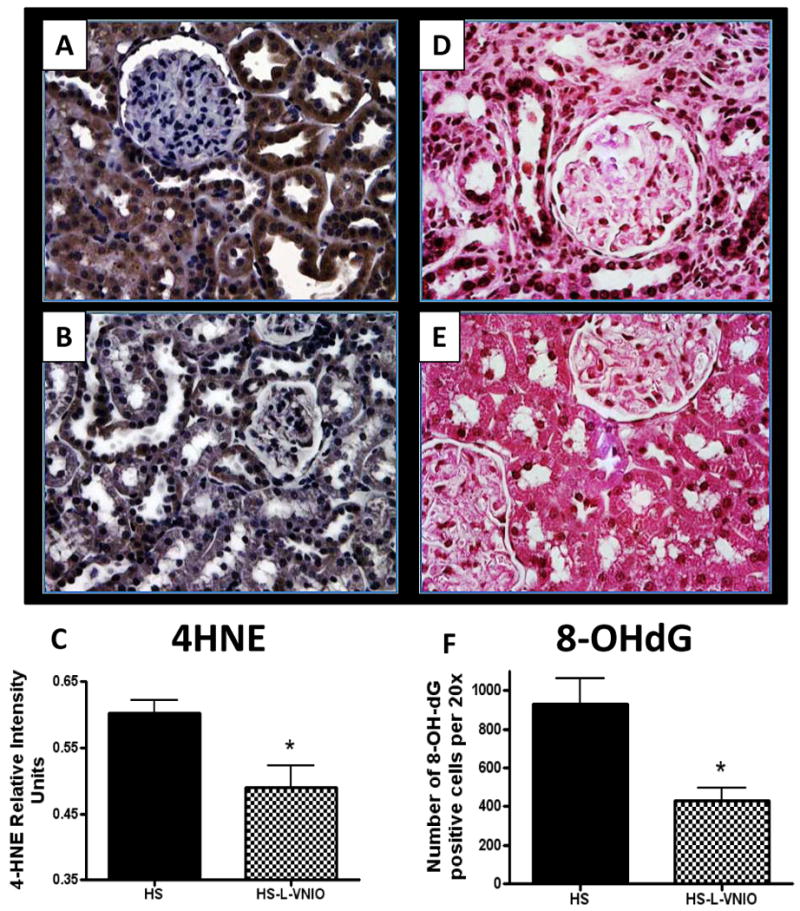
High salt may induce oxidative stress in the renal cortex by increasing nNOS expression but reducing the cofactor BH4 which may uncouple nNOS and increase superoxide production (O2-). High salt also reduces eNOS expression which may contribute to lower levels of nitric oxide (NO) and salt-dependent hypertension. The nNOS inhibitor L-VNIO may attenuate the nNOS-dependent formation of O2- to reduce renal fibrosis, inflammation, albuminuria, and renal hypertrophy without altering blood pressure.
