Figure 1.
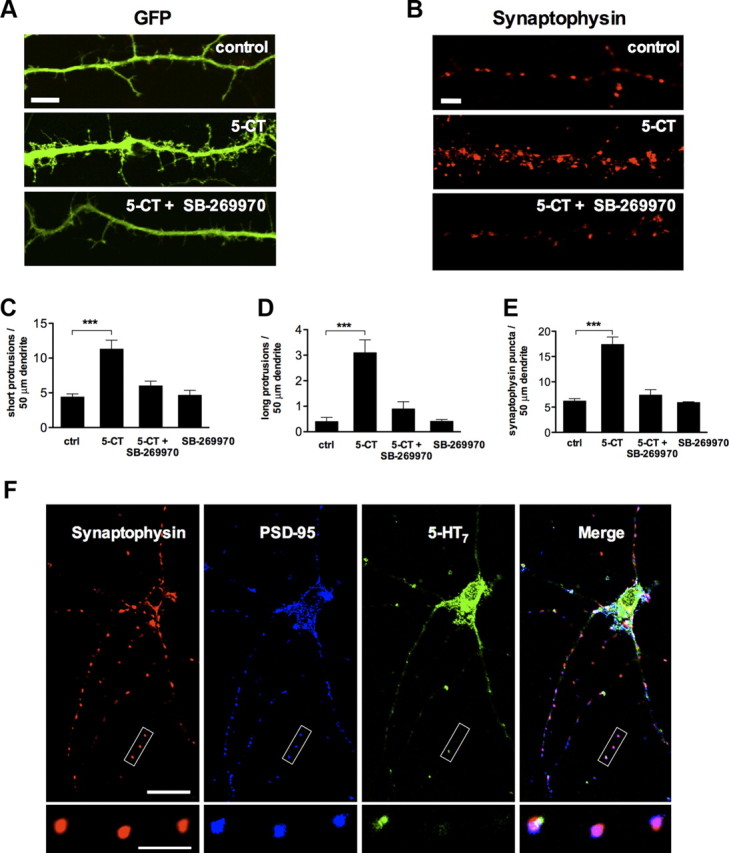
Stimulation of the 5-HT7 receptor induces formation of dendritic filopodia and synaptic clusters. A, Representative image showing dendritic morphology of control (top), 5-CT (100 nm; middle), and 5-CT (100 nm) plus SB-269970 (1 μm; bottom) treated neurons. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, Synaptophysin puncta in dendrites of control (top), 5-CT (100 nm; middle), and 5-CT (100 nm) plus SB-269970 (1 μm; bottom) treated neurons. Scale bar, 10 μm. C, D, The number of short (C; <10 μm) and long (D; >10 μm) dendritic protrusions is significantly increased in 5-CT-treated neurons compared with the control (ctrl) neurons. The morphogenic effect is receptor specific because it is inhibited by SB-269970, an antagonist of the 5-HT7 receptor. Values represent mean ± SEM; ***p < 0.001 (n = 30). E, Quantification of synaptophysin-positive puncta in control (ctrl) and in 5-CT-treated neurons. The synaptogenic effect of 5-CT is abolished after treatment with the 5-HT7 receptor antagonist SB-269970. The number of dendritic protrusions and synaptophysin-positive puncta are calculated per 50 μm of dendrite. Values represent means ± SEM; ***p < 0.001 (n = 30). F, Confocal microscope image of untreated hippocampal neurons at DIV11. The synapses formed in cultured neurons appear to be structurally intact, as defined by the colocalization of the postsynaptic density protein PSD-95 and synaptophysin puncta. Expression of the 5-HT7 receptor was observed both in cell body and dendrites. The bottom high-magnification images represent a part of the neurite where the 5-HT7 receptor is colocalized with presynaptic (synaptophysin) and postsynaptic (PSD-95) markers. Scale bars: top, 20 μm; bottom, 10 μm.
