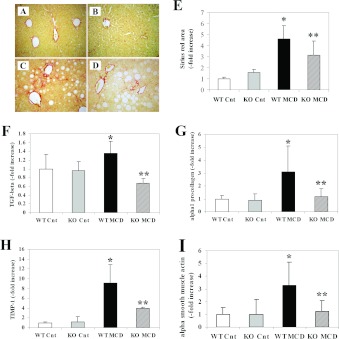
Figure 4. Effects of CCL2 deficiency on the development of fibrosis induced by an MCD diet and expression of pro-fibrogenic genes in Balb/C mice.
WT or CCL2-KO mice were fed for 8 weeks on the control diet or the MCD diet. Groups are as in the legend to Figure 1. (A–D) At the end of the study protocol, animals were killed and liver sections stained with Sirius Red. (A) WT animals fed on the control diet (WT-Cnt); (B) CCL2-KO animals fed on the control diet (KO Cnt); (C) WT animals fed on the MCD diet (WT MCD); (D) CCL2-KO animals fed on the MCD diet (KO MCD). (E) Sirius-Red-stained slides were subjected to image analysis, and the area occupied by fibrotic tissue was measured in WT and CCL2-KO mice fed on the control diet or the MCD diet. (F–I) RNA was isolated from liver tissue and the expression of TGF-β (F), type I procollagen (G), TIMP-1 (H) and α-smooth muscle actin (I) were measured by RT-PCR. *P<0.01 compared with WT animals fed on the control diet; **P<0.01 compared with WT animals fed on the MCD diet.