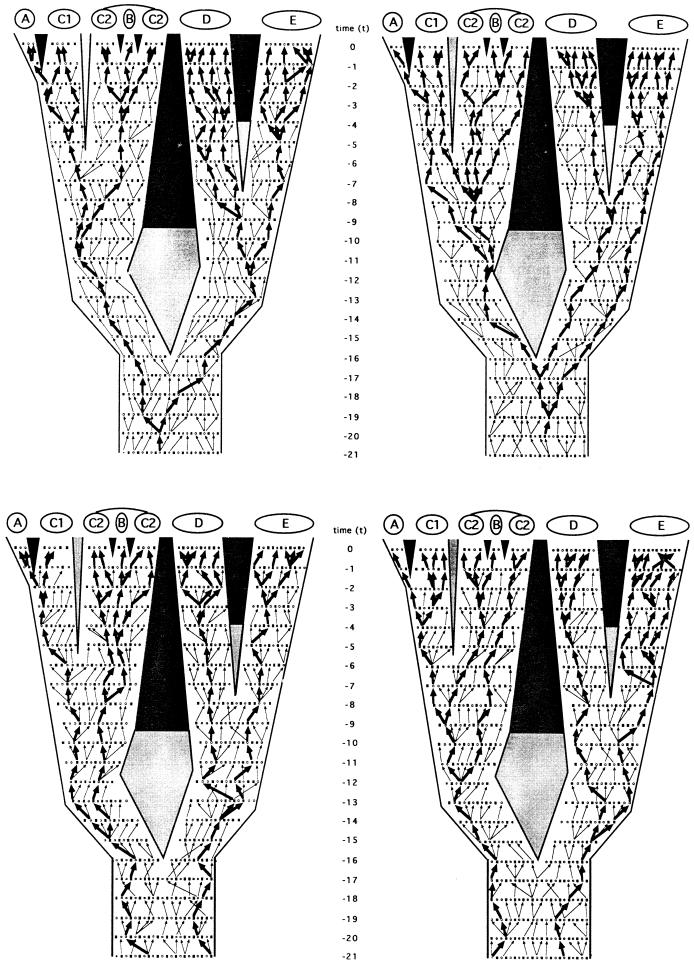
Figure 3.
Identical phylogeny and pedigree to Fig. 2, but here in which the four allelic transmission pathways that are mutually exclusive in every generation have been highlighted by arrows. (Upper Left) Matrilineal pathway reflecting the “F → F → F → F … ” transmission route (e.g., of mtDNA). (Upper Right) Patrilineal pathway reflecting the “M → M → M → M … ” transmission route (e.g., of the Y chromosome). (Lower Left) Generation-to-generation pathway through alternating genders “M → F → M → F… . ” (Lower Right) The reciprocal of the latter, “F → M → F → M… . ” Heavy arrows mark transmission routes through this pedigree that extend to the current generation; light arrows mark the same respective transmission routes that terminated before reaching the extant generation.