Figure 2.
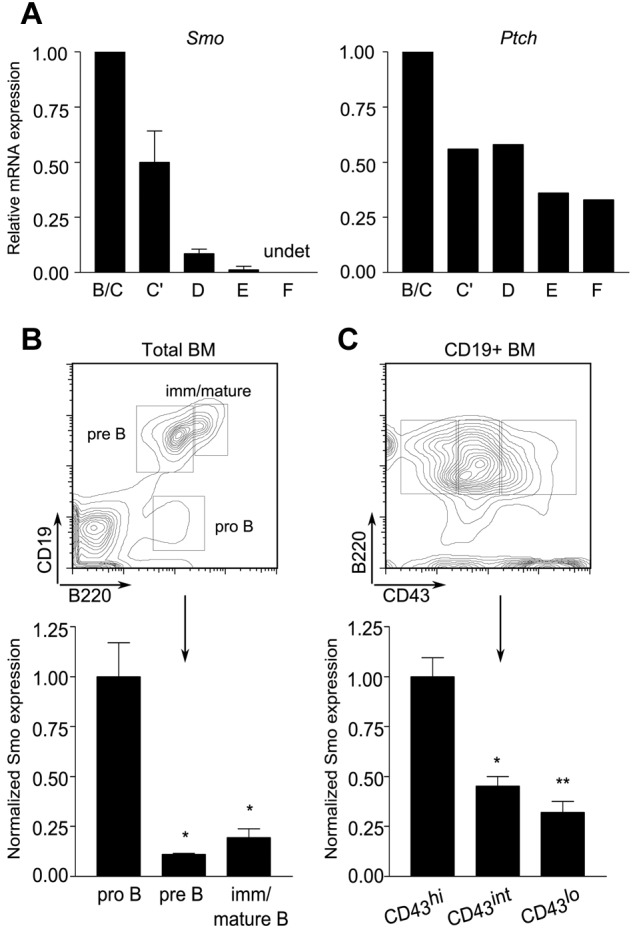
Differential expression of Hh signaling components during B-cell development. (A) Reduced accumulation Smo and Ptch transcripts as a function of B-cell ontogeny. Quantitative RT-PCR of Smo (left) and Ptch (right) transcripts in B-lymphoid developmental fractions B/C (B220+CD43+HSAintBP-1−/+), C′ (B220+CD43+HSAhiBP-1+), D (B220+CD43−IgM−IgD−), E (B220+CD43−IgM+IgD−), and F (B220+CD43−IgM+IgD+). Data for each developmental fraction were normalized to an internal Actb (β-actin) control and then to the Actb-normalized value for developmental fraction B/C. Smo expression was determined in 2 independent samples of each developmental fraction; Ptch expression was determined in one of the sample sets used for Smo. (B-C) Surface expression of Smo is attenuated at the pro-B to pre-B transition. BM cells were stained for Smo and selected B-cell developmental markers and then analyzed by flow cytometry. (B top panel) Identification of pro-B (B220+CD19−), pre-B (B220+CD19+), and immature/mature B (B220hiCD19+) subsets on a representative plot of CD19 fluorescence against B220. (B bottom panel) Surface expression of Smo on developing B-lymphoid progenitors (n = 3, *P < .01, **P = .005). (C top panel) Identification of pro-B (B220+CD19+CD43hi), transitional pro-B (B220+CD19+CD43int), and pre-B cell (B220+CD19+CD43lo) subsets. (C bottom panel) Expression of Smo as cells traverse the pro-B to pre-B transition (n = 3, *P < .01, **P = .005). Expression of Smo was normalized to that of the B220+CD19+CD43hi subset.
