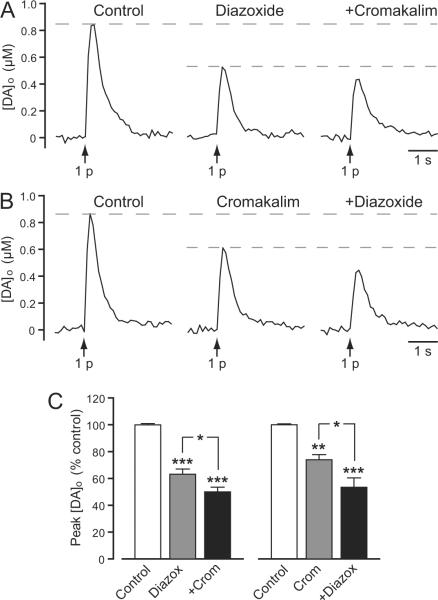
Figure 6. Presynaptic KATP channels suppress axonal DA release.
A and B. Representative [DA]o versus time records obtained in striatal slices showing the effect of SUR1 and SUR2 KATP-channel openers on DA release evoked by local single-pulse stimulation (1 p). A. Representative records of 1 p evoked [DA]o in control conditions, in the presence of the SUR1-acting KATP-channel opener diazoxide (60 μM) and in the presence of diazoxide plus the SUR2-acting KATP-channel opener cromakalim (60 μM). B. Representative records of 1 p evoked [DA]o in control conditions, in the presence of cromakalim (30 μM) and in the presence of cromakalim plus diazoxide (30 μM). C. Mean data for the effect of KATP-channel openers on peak [DA]o evoked by 1 p. Diazoxide (Diazox; 30–60 μM) decreased peak [DA]o by ~38% (***p < 0.001 vs. control); a further decrease was seen when cromakalim (Crom; 30–60 μM) was co-applied (*p < 0.05 vs. diazoxide alone) (n = 6). Cromakalim (30–60 μM) decreased peak [DA]o by ~26% (**p < 0.01 vs. control); a further decrease was seen when diazoxide (30–60 μM) was co-applied (*p < 0.05 vs. cromakalim alone) (n = 6). Data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni's multiple comparisons of selected sets.