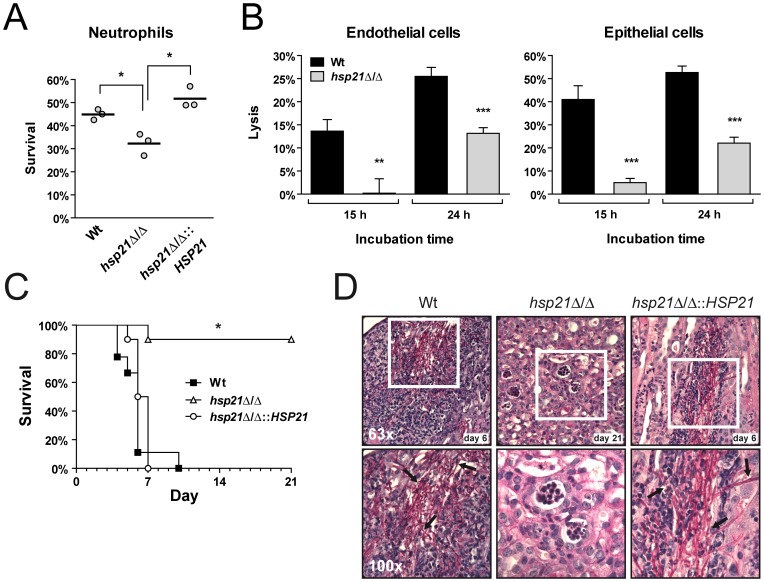
Figure 5. Hsp21 is a virulence factor.
(A) The deletion of HSP21 leads to increased susceptibility of C. albicans to killing by human neutrophils. Wild type (Wt), hsp21Δ/Δ mutant and hsp21Δ/Δ::HSP21 complemented mutant cells were exposed to human neutrophils for three hours and viability was then determined by plating on YPD agar. Experiments were performed three times. The bar represents the mean of these single values. *P<0.01 compared with the wild type and hsp21Δ/Δ::HSP21 complemented strain. (B) Hsp21 is required for C. albicans to cause full damage to endothelial and oral epithelial cells in vitro. Monolayers of human-derived endothelial and oral epithelial cells were infected with C. albicans wild type (Wt) and hsp21Δ/Δ mutant strains for 15 or 24 h. Host cell damage was then determined by measuring lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels. Results are the mean ± SD of at least three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate. **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 compared with the wild type strain. (C) The hsp21Δ/Δ mutant is avirulent in a mouse model of hematogenously disseminated candidiasis. Female Balb/C mice (n = 10 mice per C. albicans strain) were challenged intravenously with either the wild type (Wt), the hsp21Δ/Δ mutant or the hsp21Δ/Δ::HSP21 complemented strain via the lateral tail vein. *P<0.0001 compared with mice either infected with the wild type or hsp21Δ/Δ::HSP21 complemented strain. (D) Periodic acid Schiff staining of kidney sections from mice infected with the wild type and hsp21Δ/Δ::HSP21 complemented strain six days, and with the hsp21Δ/Δ mutant strain 21 days post infection. Pictures were taken at 63x (upper panel) and 100x magnification (lower panel). The lower panel of images show magnifications of the white boxed areas from the above images. Arrows point to C. albicans filaments within the tissue.