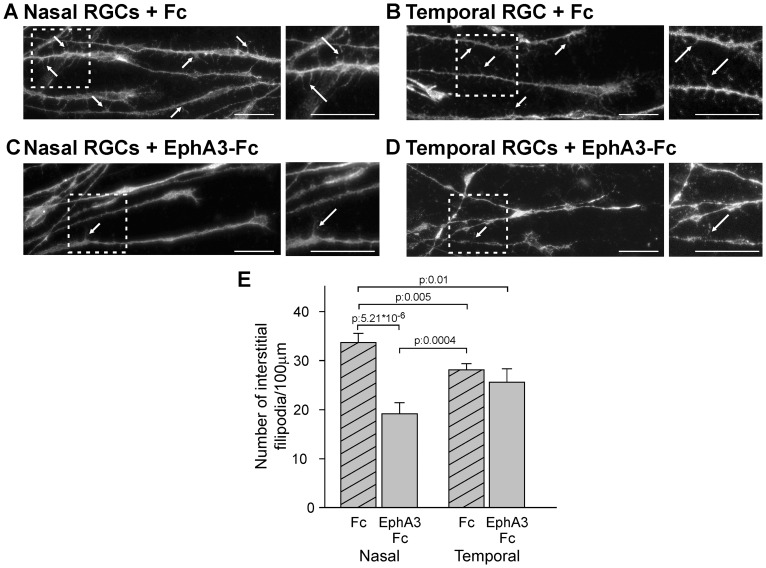
Figure 5. EphA3 ectodomain decreases the density of interstitial filopodia in nasal RGC axons.
A–D. Representative microphotographs of axons grown from nasal (A, C) and temporal (B, D) retinal explants exposed to soluble clustered Fc (A, B) or EphA3-Fc (C, D). Axons are labeled with Alexa 488-phalloidin. Arrows depict representative interstitial filopodia. Insets show filopodia at higher magnification. Scale bars = 20 µm. (E) Quantification of filopodia number/100 µm of axon shafts. Nasal axons present higher density of interstitial filopodia and EphA3-Fc significantly decreases the density of interstitial filopodia in nasal RGC (ANOVA and Tukey postest, 3 experiments, n: 8 axons for explant, 4 explants for condition). Results are shown as mean +/− SE.