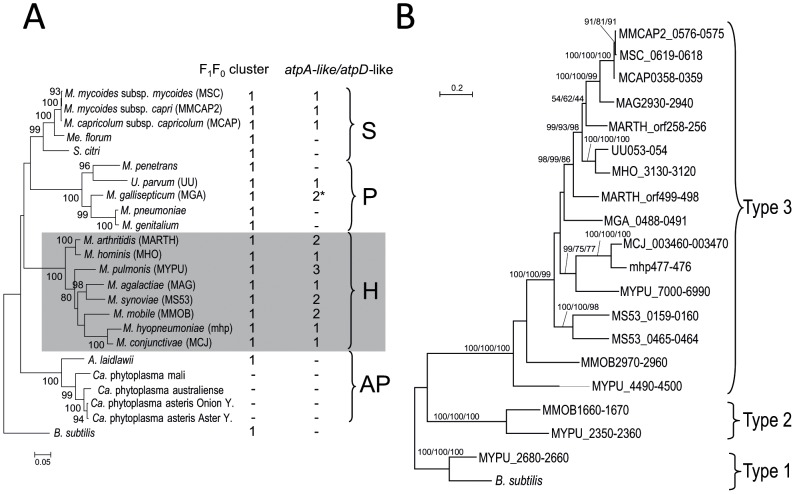
Figure 2. Distribution and evolution of extra copies of atpA-like and atpD-like genes in mollicutes.
A. The number of typical F1F0 ATPase operons and of extra copies of atpA-like/atpD-like pairs of genes are indicated for each species. * In M. gallisepticum, one of the two extra copies only contains a truncated atpD-like gene. The 16S rDNA phylogenetic tree was generated by the ML method; bootstrap values of more than 50% are indicated. Bacillus subtilis was chosen as an outgroup species. Phylogenetic groups are indicated: S, Spiroplasma; H, Hominis; P, Pneumoniae; AP, Acholeplasma/Phytoplasma. Mnemonic codes are indicated in brackets besides species names when useful. B. The amino acid sequences of the proteins encoded by the atpA-like and atpD-like genes were concatenated and a multiple alignment was generated. Protein sequences of Type 1 atpA and atpD genes from M. pulmonis and B. subtilis (GenBank ID: atpA, NP_391564.1; atpD, NP_391562.1) were used as outgroup. The multiple sequence alignment was curated with GBLOCK to remove unreliable sites and a final round of manual editing was performed with Jalview. Phylogenetic trees were generated by ML, NJ and MP methods. The tree represented was obtained by the ML method. The aLRT/Bootstrap values corresponding to these three methods are indicated on the branches, in the following order: ML/NJ/MP. Sequences are labelled by their mnemonics, see also Table S2 for details.