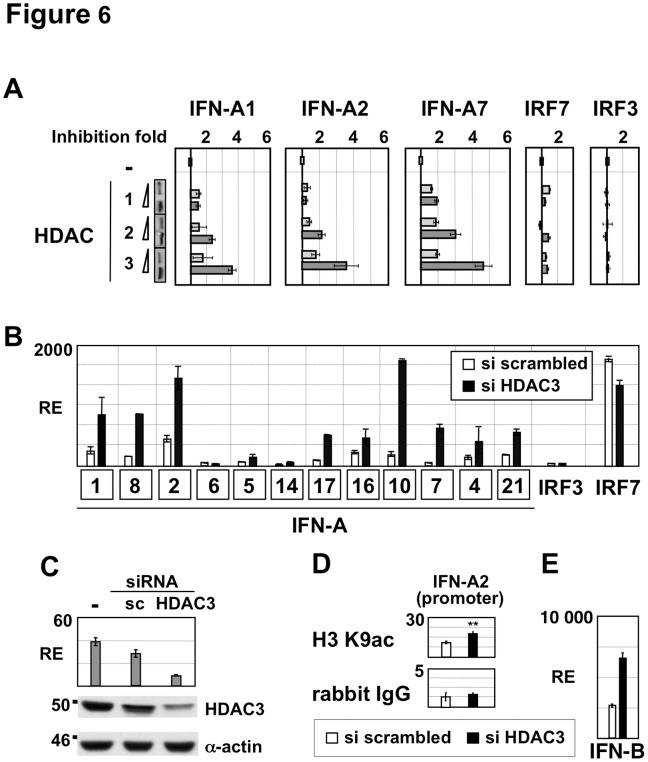
Figure 6. Inhibitory effect of HDAC3 on IFN-A gene transcription.
(A) The effect of HDACs class I (1, 2 and 3) on IFN-A gene transcription was determined in HEK293-TLR3 cells transfected with pcDNA3-IRF7A together with an HDAC-encoding plasmid added in 2-fold increasing amounts, as indicated in Materials and Methods. After 24 h of expression, the inhibition fold was calculated from IFN-A mRNA levels determined by RT-QPCR in HDAC-expressing cells in comparison to control cells transfected with pcDNA3. HDAC expression determined by anti-flag immunoblotting of the cell lysates is shown in the insets. (B) HDAC3 expression was specifically inhibited for 40 h by siRNA in HEK293-TLR3 cells expressing TRAF3 and IRF7A. IFN-A gene expression was determined after HDAC3 depletion by RT-QPCR following 8 h of infection by Sendai virus and compared to the expression determined in cells transfected with scrambled siRNA oligonucleotides. (C) Silencing efficiency was confirmed by RT-QPCR and Western blot analyses using total RNA and proteins extracted from cells transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides specific for HDAC3 or a mixture of scrambled (sc) siRNAs. (D) Histone H3K9 acetylation associated with the IFN-A2 gene promoter was determined in control and HDAC3-depleted cells by quantitative ChIP assays as described in Materials and Methods. Anti-rabbit IgG was used to determine non-specific binding. (E) IFN-B gene expression was determined by RT-QPCR following 8 h of infection by Sendai virus in HEK293-TLR3 cells expressing TRAF3 and IRF7A and transfected with scrambled siRNA or siRNA oligonucleotides specific for HDAC3.