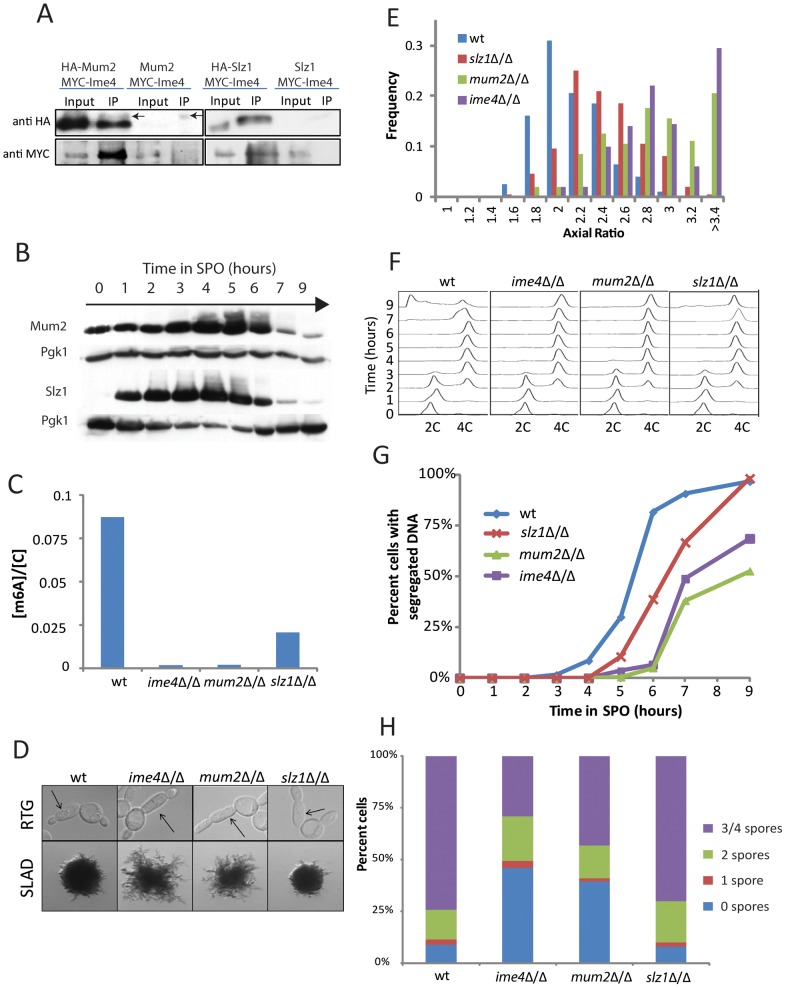
Figure 5. Mum2 and Slz1 interact with Ime4 and are required for m6A formation.
A) Western analysis for co-immunoprecipitation of Mum2 (left panels) and Slz1 (right panels) with Ime4. HA-tagged Mum2 or Slz1 was immunoprecipitated from cellular extracts 3 hours after induction of meiosis and probed for interaction with myc-tagged Ime4 (SAy1232, SAy1253, respectively). A myc-Ime4 (SAy914) strain without HA-tags served as a control. Arrows in the IP lanes indicate IgG bands. B) Western analysis for HA-tagged Mum2 protein (SAy1235) or HA-tagged Slz1 protein (SAy1254) throughout meiosis; Pgk1 protein serves as loading control. C) Quantification of m6A on mRNA three hours after meiotic starvation, when m6A accumulation is maximal in wild-type cells (SAy821). Deleting any one of ime4Δ/Δ (SAy771), mum2Δ/Δ (SAy1196) and slz1Δ/Δ (SAy1206) results in a reduction in m6A levels. D) Wild-type (SAy821), ime4Δ/Δ (SAy771), mum2Δ/Δ (SAy1196) and slz1Δ/Δ (SAy1206) daughter cell morphology upon RTG3 (top panels). Arrows indicate primary buds. The same strains were photographed after growth on SLAD for 6 days (bottom panels). E) Axial ratio quantification of primary daughter cells upon RTG3 for strains in (D). (F) FACS analysis of DNA synthesis in strains from (D) throughout a meiotic time course (n = 3×104 cells/strain/time point). DNA content of diploid cells before DNA replication (2C) and after DNA replication (4C) is indicated. G) Kinetics for meiotic nuclear divisions as assayed by DNA staining by DAPI in the strains from (C) (n = 200 cells/strain/time point). H) Number of asci with one, two, three/four, or no spores in strains from (D) after 24 hours in SPO medium (n = 200 cell/strain).