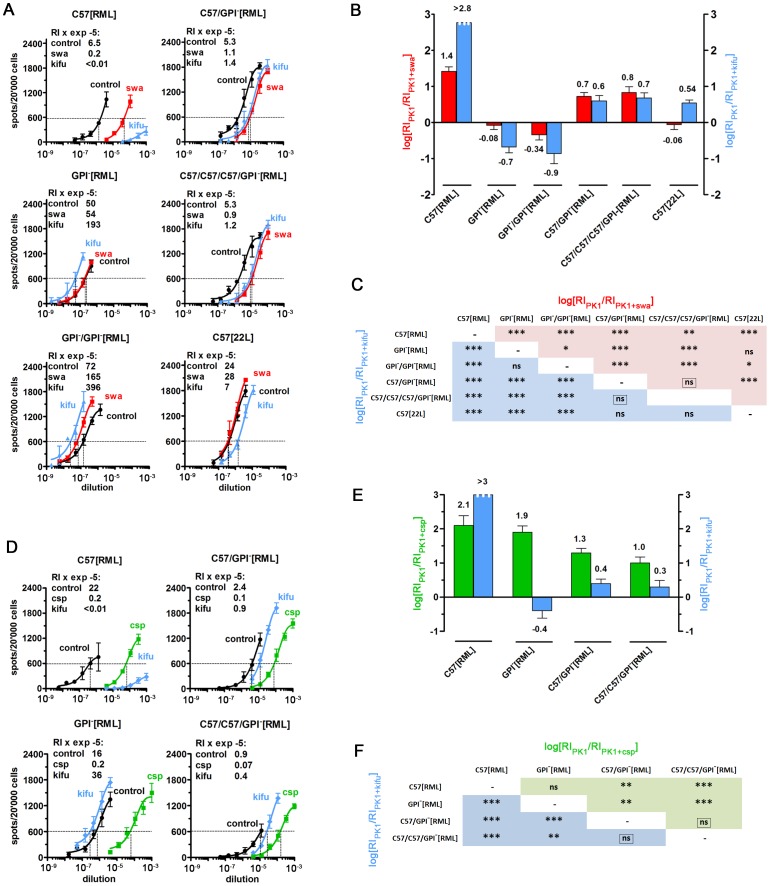
Figure 3. RML prions propagated in tgGPI− mice and returned to wild-type mice emerge as a novel, stable strain.
Analysis of authentic RML prions propagated in C57BL/6 brain (C57[RML]), and of RML prions first propagated in GPI− brain (GPI−[RML]) and then once (C57/GPI−[RML]), twice (C57/C57/GPI−[RML]) or three times (C57/C57/C57/GPI−[RML]) in C57BL/6 brain. (A) shows the SSCA performed on PK1 cells in the presence or absence of kifunensine (kifu; 5 µg/ml) or swainsonine (swa; 2 µg/ml) for the samples indicated; C57[22L] was added as control. RI's were determined at 600 spots (RI600). Kifu strongly inhibited the propagation of C57[RML], but not of C57/GPI−[RML] and C57/C57/C57/GPI−[RML] prions on PK1 cells. (B) The bar graph shows the log[RIPK1/RIPK1+kifu] and log[RIPK1/RIPK1+swa] values for the samples listed in (A). The pairwise comparison in panel (C) shows that C57/GPI−[RML] and C57/C57/C57/GPI−[RML] prions do not differ significantly, but are vastly different from C57[RML] and GPI−[RML] prions. The framed “ns” indicates high p values (>0.1) for both log[ratios], indicating no significant difference between the samples. (D) Effect of castanospermine (csp; 50 µg/ml) or kifu (5 µg/ml) on propagation of the samples indicated on PK1 cells. As in (A), kifu strongly inhibits the propagation of C57[RML], but not C57/GPI−[RML] and C57/C57/GPI−[RML] prions. The same is true for csp, however to a lesser extent. (E) The bar graph depicts the log[RIPK1/RIPK1+kifu] (blue) and log[RIPK1/RIPK1+csp] (green) values. The RIPK1/RIPK1+kifu ratio was >500-fold lower for C57/GPI−[RML] and C57/C57/GPI−[RML] than for C57[RML] prions, again underscoring the difference between RML prions and the novel strain. The matrix (F) also shows that C57/GPI−[RML] and C57/C57/GPI−[RML] prions do not differ from each other, but that both differ significantly from C57[RML] prions. In summary, the figure sustains the conclusion that a new strain, designated SFL, emerged after RML prions were passaged through GPI− brain and returned C57 brain, and that they remained unchanged after two further passages.