FIGURE 8.
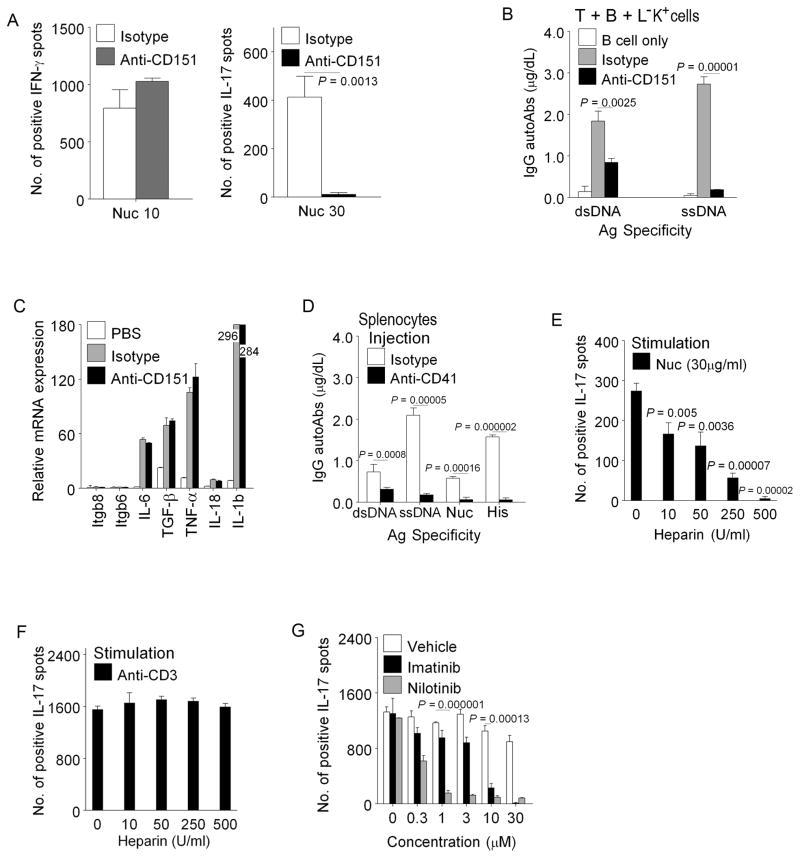
Certain agents block Th17 induction by MM (c-Kit+CD151+CD41+) cells. (A) Inhibition of nucleosome-specific Th17 response by anti-CD151: Lin−c-Kit+CX3CR+ (left) or Lin−c-Kit+CX3CR1− (right) APC subsets and T cells from SNF1 spleens were incubated with nucleosomes and CD151 antibody or isotype control, in IFN-γ and IL-17 response assays. The former subset induces Th1 and the latter induces Th17 (previously shown in Fig. 5 B–C). (B) Anti-CD151 antibody (100μg/ml) suppressed IgG autoantibody production in nucleosome-stimulated helper assay. T+B cell co-cultures without nucleosomes produce very little autoantibodies in these helper assays as previously shown in Fig. 4 A (T+B+B). (C) Blocking with anti-CD151 antibody did not affect mRNA expression of integrins (beta 6 and 8) and Th17 inducing cytokines by nucleosome pulsed Lin−c-Kit+pure cells. (D) Splenocytes from 4 mo old SNF1 mice injected with anti-CD41 antibody produced markedly reduced amount of IgG autoantibodies ex vivo in nucleosome stimulated cultures, as compared to isotype control injected mice. (E) Heparin inhibited Th17 response to nucleosomes presented by MM cells in ELISPOT assays. (F) Heparin could not inhibit Th17 response to anti-CD3 stimulation. (G) c-Kit inhibitors (Imatinib or Nilotinib) inhibited MM induced nucleosome-specific Th17 responses. Mean ± s.e.m. from 3 independent experiments. n= 15 mice.