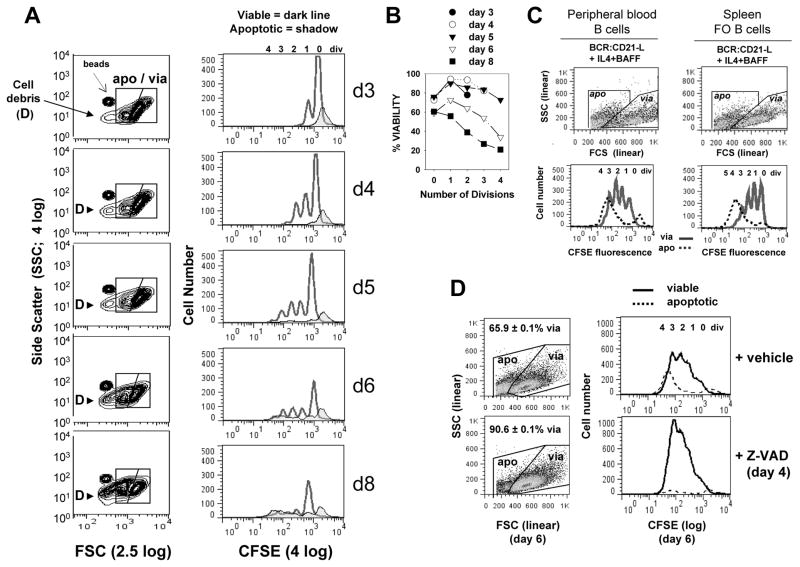
FIGURE 1. Kinetics of caspase-dependent AICD following human B cell clonal expansion in response to surrogate C3d-coated Ag (BCR:CD21-L), IL-4 and BAFF.
(A) CFSE-labeled, resting B cells were cultured with a limiting dose of BCR:CD21-L (0.01 μg/ml) + IL-4 and BAFF. Following varying culture intervals, cultures were pulsed with a known quantity of Autocomp beads, harvested, fixed with 2% formaldehyde, and analyzed by flow cytometry. 20,000 total events were acquired at each time point and FSC and SSC were evaluated on a log scale (left column, Figure 1A). This enabled detection of Autocomp beads (which have a lower FCS than the standardization beads used for assessing cell recovery in all other experiments (CountBright absolute counting beads; Invitrogen)). It also revealed that subcellular particles (debris = D) rise substantially after day 5 (6). For analysis of the divisions represented within intact viable and apoptotic cells (right column), events were gated on the basis of light scatter (as seen in left column) and analyzed for level of CFSE-fluorescence: dark lines = viable, tinted histogram = apoptotic. As described earlier (6), a fraction of undivided cells succumbs to death during the first 2 days of culture (far right apoptotic peak in CFSE histograms). These retain the high levels of CFSE present at the time of their demise and are unlikely related to activation, since they are seen at greater levels within non-stimulated cultures containing medium alone (6). (B) Calculations for % viability within each division subset of total intact cells (viable + apoptotic) were made from the cultures in Figure 1A, as described in our earlier studies (5, 6) and in the present materials and methods. It should be noted that these % viability determinations are not fully accurate because they do not account for the significant number of apoptotic cells which fragment into debris (D) and are excluded from consideration Nevertheless, the % viability calculations are valuable because they demonstrate that survival of highly divided progeny diminishes with time. (Note: % viability as determined by FSC/SSC-based gating of these cultured cells is comparable to % viability determinations on the basis of FITC-annexin V/PI staining (127) or PE-annexin/7-AAD staining (Supplementary Figure 1). (C) CFSE-labeled peripheral blood B cells and splenic FO B cells were cultured with BCR:CD21-L + IL-4 + BAFF for 5 days, gated into apoptotic and viable subsets as shown and evaluated for CFSE fluorescence. (In these and all subsequent experiments, FSC and SSC are plotted on linear scales, with the FSC threshold setting excluding most debris.) Similarly to activated tonsil FO (B2) cells, both these latter populations show evidence of significant AICD in replicating blasts (D) Cultures of activated B cells received a day 4 pulse of pan-caspase inhibitor, Z-VAD-FMK (40 μM), or DMSO vehicle control. Cultures were harvested on day 6, fixed, and analyzed by flow cytometry, Scatter plots to left show the gating of viable and apoptotic cells and the % viability values of replicate cultures within the experiment (mean ± SEM). Histograms to right represent day 6 CFSE fluorescence profiles for viable (solid) and apoptotic (dashed) cells. (Results representative of > 3 exps)