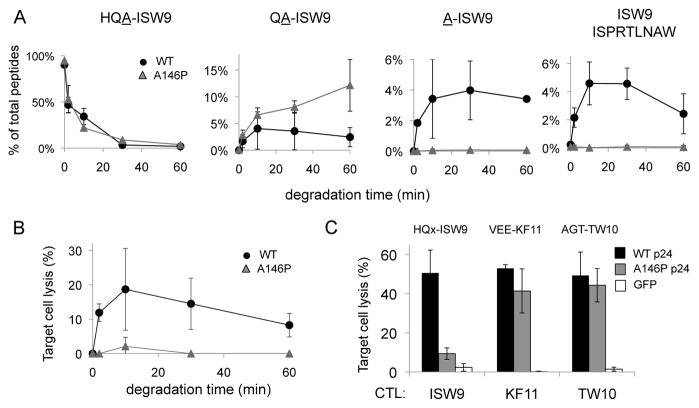
Figure 4. An HLA-restricted epitope-flanking mutation toward a poorly cleavable aminopeptidase motif impairs epitope production and presentation.
A. Peptide corresponding to HLA-B57-ISW9 with a 3-residue extension with WT (HQA-ISW9, black circles) or mutated HQP-ISW9 (grey triangles) were degraded in PBMC cytosol. The relative amount of 3-, 2-, 1-extended and epitope ISW9 (left to right) was identified by mass spectrometry over 60 minutes. The relative amount of each peptide in the total mix of degradation products is quantified at each time point. Average of 2 degradation experiments run twice on a mass spectrometer. 2 additional degradation experiments with less cytosol gave similar results albeit with slower degradation rates (not shown).
B. Degradation products from HQA-ISW9 (black circles) or HQP-ISW9 (grey triangles) of each time point were pulsed onto HLA-B57 cells used as targets in a chromium assay with ISW9-specific CTL. Average of 3 killing assays run in triplicates.
C. HLA-B57 cells were transfected with RNA encoding WT p24 (black bars), p24 with A146P mutation flanking ISW9 (grey bars) or GFP (white bars) and used as targets in a chromium-based killing assay with ISW9-, KF11, or TW10-specific CTL (3 epitopes located in p24 and restricted by HLA-B57). Epitope flanking sequences indicated above bars. Average of 3 transfections; killing assays run in triplicates.