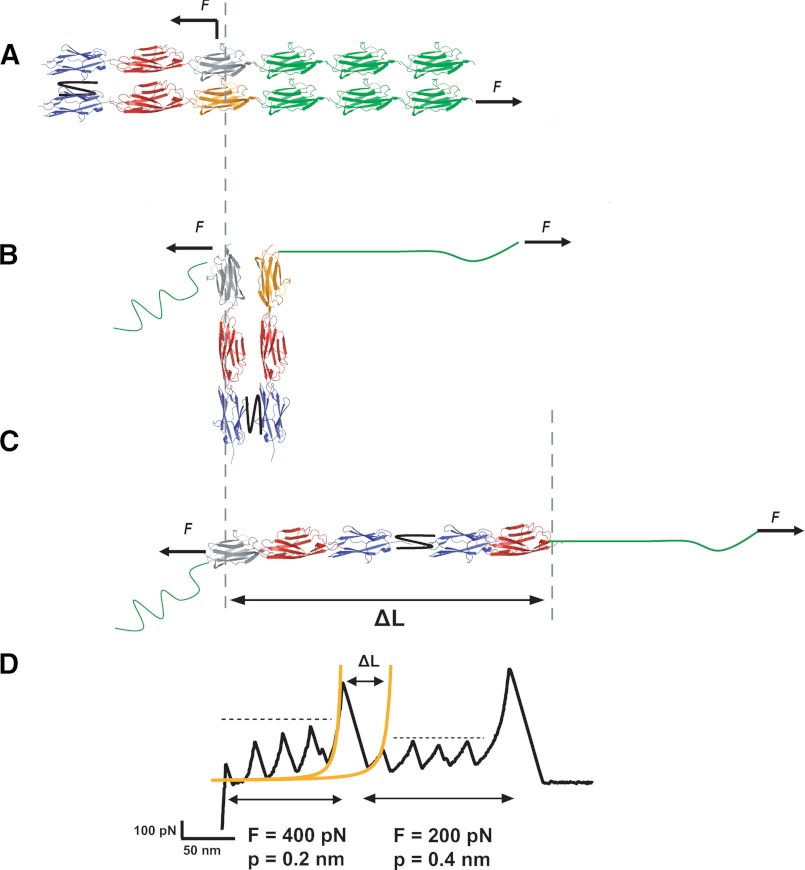
FIGURE 6.
Schematic model of force-induced dimer-to-monomer mechanism. A, pulling the protein dimer from random positions along a different pulling direction results in the parallel in-register unfolding of three I27 modules (green). B, during this process, the protein will rotate, forming an angle up to 90° with the pulling direction. C, the pulling force will then disrupt the interface between the two parallel polyprotein chains forming the dimer, forcing the protein to rotate until it aligns with the pulling force. D, this process increases the contour length of the protein, ΔL, by an amount equal to the length released upon unfolding of one domain (orange monomer in panel B) plus the length gain corresponding to the number of monomers that remained folded.