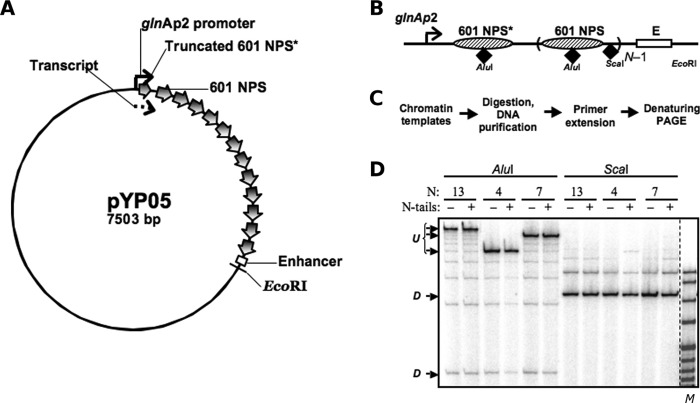
FIGURE 1.
Nucleosome positions and occupancies on saturated 601 arrays. A, schematic diagram of the pYP05 template. The 601 nucleosome-positioning sequences are indicated by wide arrows. The glnAp2 promoter and the enhancer are positioned over 0.7–4.5-kb distances from each other (2.5 kb in the image). The first 601 nucleosome-positioning sequence (601 NPS*) is truncated by 35 bp from the 3′ end and overlaps with the 176-nucleotide transcript (dashed arrow). B, schematic map of the arrays containing different numbers N of 601 nucleosome-positioning sequences (NPS) between the glnAp2 promoter and the enhancer (E). AluI sites for restriction endonucleases are located close to the middle of the positioning sequences, and ScaI sites are in the middle of the 30-bp DNA linkers. C, experimental approach: a restriction enzyme sensitivity assay with primer extension. Chromatin was assembled on a negatively supercoiled pYP05 plasmid and digested with an excess of restriction enzymes AluI or ScaI. Purified DNA was next digested with EcoRI restriction endonuclease to create one DNA end and then subjected to primer extension using a promoter-proximal end-labeled primer. D, characterization of the 601177×13 saturated nucleosomal arrays assembled on pYP05 using the restriction digestion sensitivity assay. Analysis of primer end-labeled DNA by denaturing PAGE was performed. Undigested (U) and fully digested (D) DNA fragments are indicated. Note that the increase in the chromatin assembly level results in almost quantitative protection of the templates from AluI, but not ScaI restriction enzyme. M denotes the MspI digest of pBR322 plasmid.