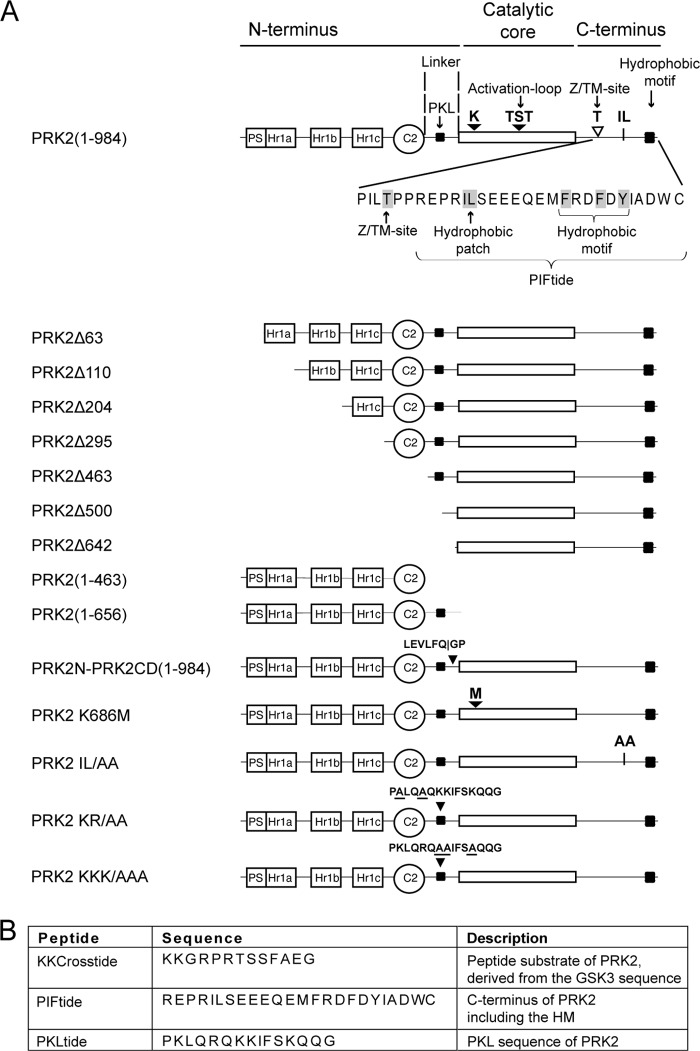
FIGURE 1.
Schematic representations of PRK2, PRK2-derived proteins, and peptides employed in this study. A, the potential pseudosubstrate region (PS), the Rho-binding domains (Hr1a, Hr1b, Hr1c), the C2-like domain (C2), and the PKL sequence (PKL) are indicated. A close up of the C-terminal region of PRK2(1–984) shows the Z/TM site, the hydrophobic IL patch, and the hydrophobic motif. Proteins were expressed with an N-terminal GST-FLAG tag. Wild-type PRK2(1–984) was also expressed with an N-terminal FLAG tag, an N-terminal GST tag, an N-terminal His tag or a C-terminal HA tag, respectively. Additionally, N-terminal-truncated PRK2 proteins were expressed with an N-terminal FLAG tag. GST-PRK2N-PRK2CD-His contains the cleavage site of PreScission protease (LEVLFQGP). In the kinase-dead mutant PRK2 K686M, the active site lysine was mutated to methionine. The IL/AA mutant carried alanine substitutions at the hydrophobic patch Ile965–Leu966. Two additional mutants used in this study (PRK2 KR/AA and PRK2 KKK/AAA) carried alanine substitutions in the PKL region (amino acids 487–501, PKLQRQKKIFSKQQG). B, list of key peptides used in this study.