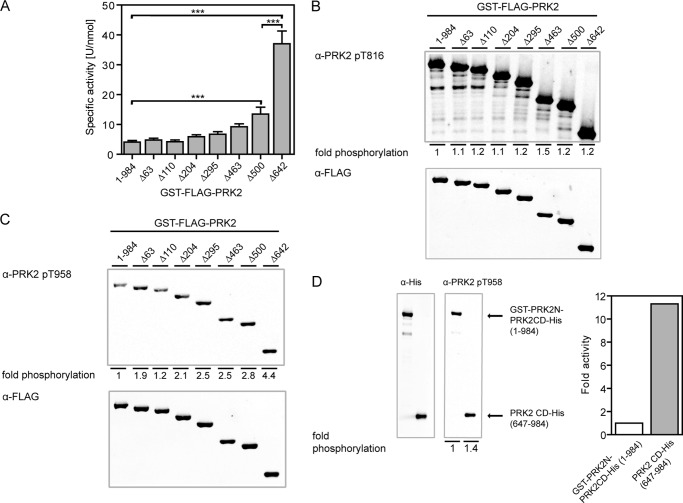
FIGURE 3.
The N-terminal region of PRK2 inhibits its kinase activity. A, the specific activity of wild-type and N-terminal-truncated GST-FLAG-PRK2 proteins purified from HEK 293T cells was measured in vitro; ***, p < 0.001 (n = 9). B and C, levels of activation loop (B) and Z/TM site (C) phosphorylation of N-terminal-truncated PRK2 proteins. Purified GST-FLAG-PRK2 proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting using phosphospecific antibodies for the activation loop site (T816; B) and the Z/TM site (T958; C). The immunoblot shown is representative for four experiments and the statistical evaluation is presented in supplemental Table S2. D, GST-PRK2N-PRK2CD-His, which contained the PreScission protease cleavage site between amino acids 646 and 647, was cleaved with PreScission protease to release the catalytic domain of PRK2 (amino acids 647–984; PRK2CD-His). Both uncleaved GST-PRK2N-PRK2CD-His and PRK2CD-His were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting using a phosphospecific Z/TM site antibody or a His tag antibody, respectively, and analyzed as described for B and C. The kinase activity of the respective proteins was measured in vitro using KKCrosstide as a substrate, and the signal was normalized to the protein amount used to measure kinase activity, which was analyzed by SDS-PAGE and quantified by immunoblotting using fluorescently labeled secondary antibodies.